2025 Major Events in the Polyurethane Industry - Highlighted Events Edition

In 2025, the polyurethane industry still failed to shake off the sluggish cycle. Despite manufacturers in Europe, Japan, and South Korea continuously selling off or shutting down polyurethane assets, the capacity expansion of key polyurethane raw materials in China has not halted.
With the continuous improvement of polyurethane raw material production capacity in China, a stable supply chain has gradually formed, capable of withstanding the impact of sudden events. The previous volatility in prices, characterized by large fluctuations, will no longer exist, and various links in the industry chain are also seeking suitable profit margins. It is encouraging that the expansion of capacity is not only focused on traditional polyurethane raw materials, but also on sustainable low-carbon polyurethane raw materials, which are being realized on a large scale in China.
As China's polyurethane raw materials and end products accelerate their overseas expansion, multiple countries have initiated anti-dumping investigations into related products in 2025, posing new international trade challenges for the industry. Among them, the United States has launched an anti-dumping investigation into Chinese MDI products and has made a preliminary ruling, with a maximum identified dumping margin reaching 511.75%. Meanwhile, India has also initiated an anti-dumping investigation into Chinese TPU paint protection film products, marking the first time TPU paint protection film products have encountered anti-dumping investigations abroad.
Now, let's take a look back at the hot events that occurred in the polyurethane industry in 2025.
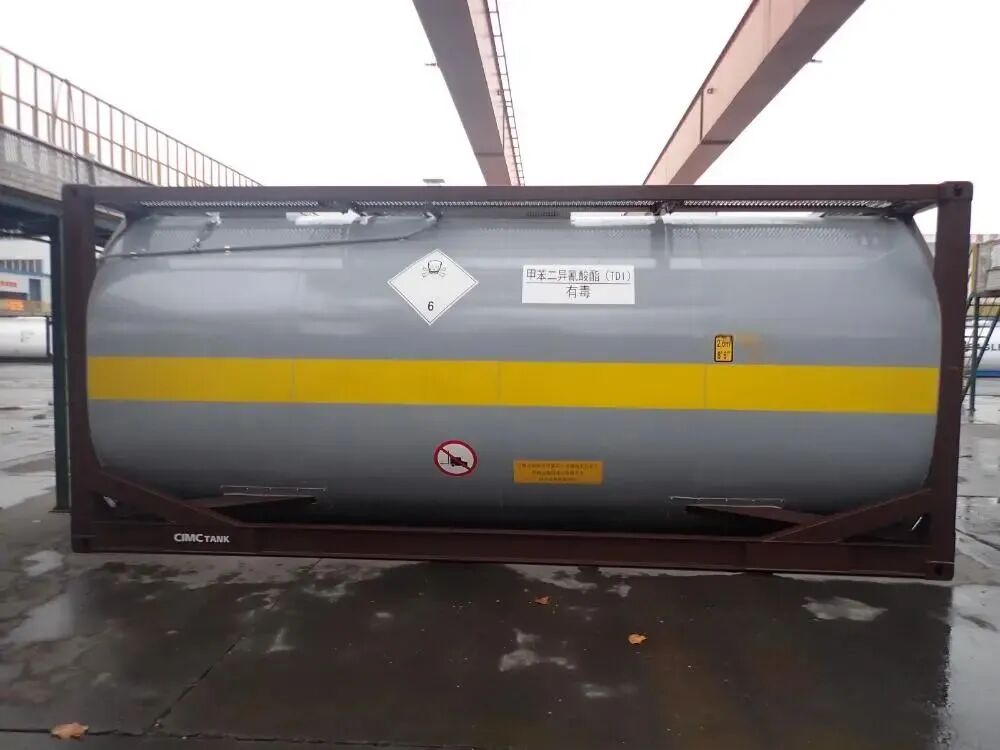

Toluene diisocyanate (TDI) is a key chemical raw material for polyurethane foam used in sofas, mattresses, and car seats. TDI has a "bad temper"; it reacts violently with water, alcohols, or strong alkaline substances, which could lead to explosions or toxic gas leaks. Therefore, it must be transported in specially designed "armor."
Currently, China has become the largest TDI production base in the world, but it has long faced transportation challenges. The high costs and risks associated with road and rail tank container transportation severely restrict transportation efficiency.
In August 2025, it was reported that CIMC Runtong, a subsidiary of CIMC Group, successfully passed static strength and impact tests for the first domestic TDI hazardous goods railway tank container developed in collaboration with a large domestic chemical enterprise. This technological innovation is akin to creating a "safety cabin" tailored for TDI, enabling hazardous chemicals to safely "ride the train" and strongly promoting the shift of hazardous chemical transportation from road to rail in China.
With the implementation of the national "Action Plan for Effectively Reducing Logistics Costs in Society," "road-to-rail" transportation has become an important direction for the transportation of hazardous chemicals. Railway transportation has advantages such as large capacity, strong stability, and low carbon emissions. However, there has been no specialized railway tank container technology for TDI in the country before.
As early as 2023, CIMC Environmental Technology collaborated with a large domestic chemical company to jointly develop TDI hazardous material tank containers suitable for China Railways.
To ensure the reliability of tank containers under extreme conditions, the research and development team conducted rigorous tests on July 7, 2025, in accordance with Chinese railway hazardous materials transportation standards, witnessed by multiple parties.

Static strength test
Load a sample 20-foot TDI tank container with equal density saline water to simulate a full load of 30 tons of cargo under static load conditions, and verify the strength, load-bearing capacity, and other performance indicators of the tank container components.
Impact Test
Impact the end of the tank container with a crash vehicle at a certain speed to test its impact resistance and evaluate the tank container's ability to withstand railway transportation conditions and complex loading scenarios.
Test results indicate that this 20-foot tank container successfully passed the 30-ton static strength test and the 8 km/h impact test, with all indicators meeting the relevant railway standards. In addition, due to the highly reactive characteristics of TDI, the tank container underwent water pressure and air tightness tests to ensure that the risk of leakage is completely eliminated.
Compared to traditional road and rail drum transportation, new technologies not only significantly enhance the safety of TDI transport but also enable the recycling of tank containers,. Currently, relevant parties are accelerating the approval process for railway operating qualifications. Once this type of tank container is put into commercial operation, it will inject strong momentum into the safety assurance and green low-carbon transition of China's chemical industry chain.

Starting from May 1, 2025, 13 mandatory national standards for energy consumption limits will be officially implemented. These standards cover multiple key industries in the national economy, including chemical, coal, mining, and papermaking. They specify the energy consumption limit levels, technical requirements, statistical scope, and calculation methods for relevant products. They are applicable to the calculation of energy consumption limits for production enterprises and the energy consumption management of new, rebuilt, or expanded projects. This will effectively promote the elimination of outdated production capacity and guide enterprises to enhance energy efficiency through energy-saving renovations, optimizing process routes, and conducting energy efficiency benchmarking.
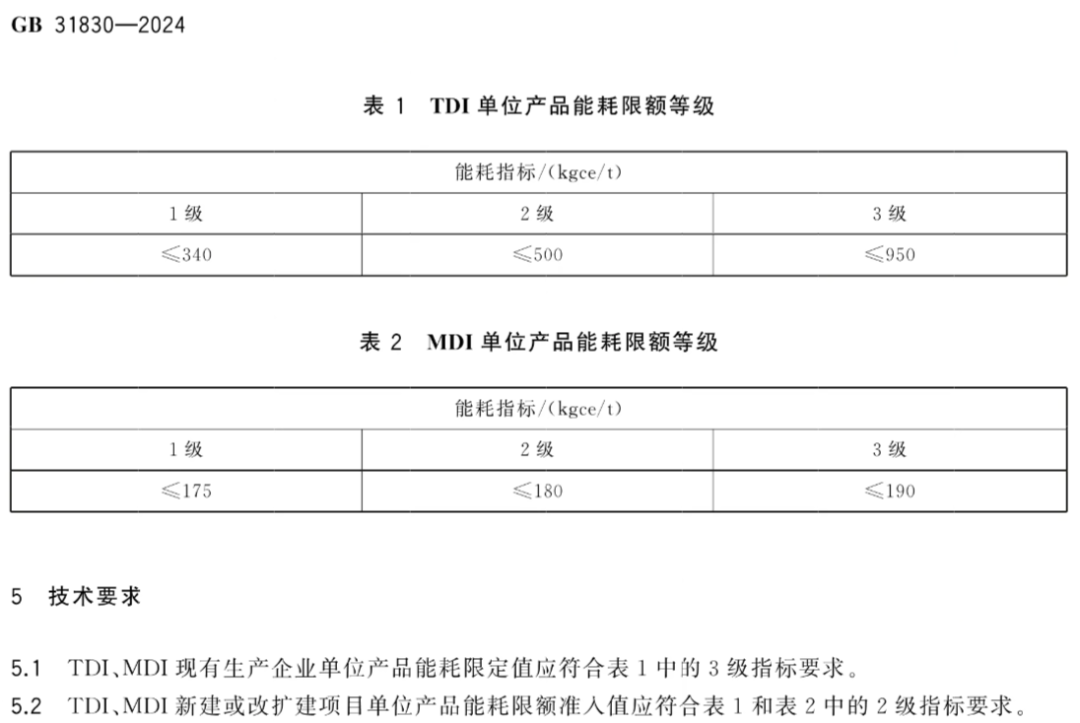
Among them is GB 31830-2024 "Energy Consumption Limits for Unit Products of Toluene Diisocyanate (TDI) and Diphenylmethane Diisocyanate (MDI)."
As of now, there are 61 effective mandatory national standards for energy consumption limits in China, covering key industries such as steel, building materials, petrochemicals, non-ferrous metals, coal, electricity, thermal energy, mining, and light industry. This essentially achieves full coverage of high energy-consuming industries, and the relevant standards provide strong support for promoting large-scale equipment upgrades and achieving energy-saving and carbon reduction goals.
In the mandatory national standard GB 31830-2024 "Energy Consumption Limit for Unit Products of Toluene Diisocyanate (TDI) and Diphenylmethane Diisocyanate (MDI)," the energy consumption limits for TDI and MDI are as follows:


In September 2025, the Jingzhou Ecological Environment Bureau announced the acceptance of the environmental impact report for the 300,000 tons/year TDI project of Hualu Hengsheng (Jingzhou) Co., Ltd.
According to the company's 14th Five-Year Development Plan, Hualu Hengsheng (Jingzhou) Co., Ltd. plans to invest approximately 46 billion yuan to establish the Hualu Hengsheng Jingzhou Base in the Jiangling Chemical Park in Jingzhou City. The Jingzhou Base will become a key focus for Hualu Hengsheng's development and a major platform for national industrial layout, serving as the main battlefield for the group's long-term industrial development. It will focus on extending the industrial chain and vigorously developing new chemical materials, new energy industry supporting materials, and high-end chemicals. The Jingzhou Base plans to revolve around the theme of clean and efficient utilization of coal, using the first-phase project as a foundation and adopting self-developed TDI production technology. It plans to implement a 30×2 thousand tons/year TDI project, ultimately forming a diversified and high-end product modern chemical enterprise, enhancing the company's competitiveness, and aiding Hualu Hengsheng in achieving leapfrog development.
The Jingzhou base is divided into three phases: Phase I, Phase II, and Phase III. Phase I has implemented the park gas dynamics platform project, the syngas comprehensive utilization project, and the melamine resin monomer material project in stages. Phase II is currently constructing an integrated project with an annual production capacity of 200,000 tons of BDO, 160,000 tons of NMP, and 30,000 tons of PBAT biodegradable materials, a 100,000 tons/year acetic acid pyrolysis method for producing acetic anhydride project, a 200,000 tons/year monoacid project, and has initiated preliminary work on a 100,000 tons/year methyl acetate project. Phase III is the newly added plot for this environmental assessment, proposed to implement the "300,000 tons/year TDI project" and reserve land for long-term development.
Project Overview
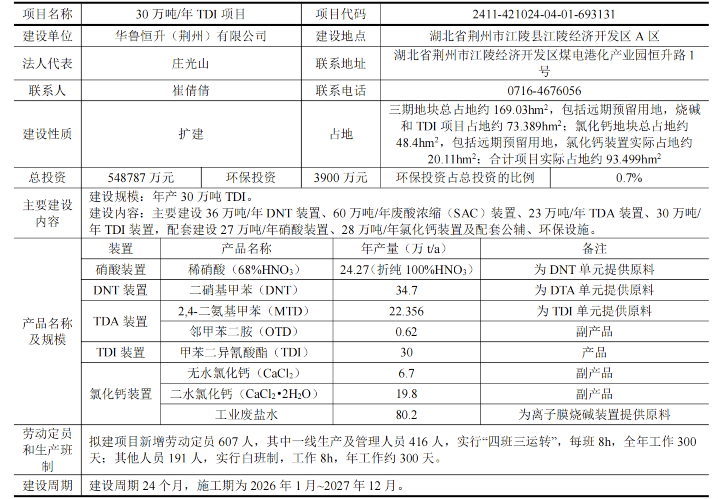
Construction Content: Mainly constructing a 360,000-ton/year DNT unit, a 600,000-ton/year waste acid concentration (SAC) unit, a 230,000-ton/year TDA unit, and a 300,000-ton/year TDI unit. Supporting construction includes a 270,000-ton/year nitric acid unit, a 280,000-ton/year calcium chloride unit, along with auxiliary and environmental protection facilities.
Project Investment: Total investment of 5,487.87 million yuan, environmental protection investment of 39 million yuan, environmental protection investment accounts for 0.7% of the total investment.

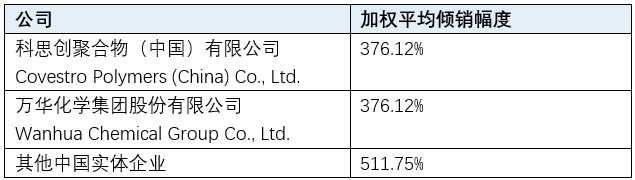
On September 11, 2025, the U.S. Department of Commerce announced a preliminary affirmative determination in the anti-dumping investigation concerning diphenylmethane diisocyanate (MDI) originating from China.
In the preliminary anti-dumping announcement, the U.S. Department of Commerce determined that the dumping margin for Chinese MDI is as high as 511.75%. From the date of the preliminary anti-dumping announcement, the U.S. Department of Commerce will instruct the U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) to impose temporary anti-dumping duties in the form of cash deposits based on the dumping margins of the relevant producers/exporters involved.
The weighted average dumping margins determined in the preliminary anti-dumping announcement are as follows:
Key Timeline of the U.S. Anti-Dumping Case on Chinese MDI
On February 12, 2025, at the request of BASF and Dow, the United States Special MDI Fair Trade Alliance (referred to as "the Alliance" or "the Petitioner") submitted a petition for new anti-dumping (AD) and countervailing duty (CVD) applications against imports of methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI) from China. At that time, the dumping margins calculated by the petitioner were estimated to range between 305.81% and 507.13%.
On March 28, 2025, more than a month after launching an investigation into allegations of China dumping MDI in the U.S. market, the United States International Trade Commission (USITC) determined that there was reason to continue the investigation.
On September 11, 2025, the U.S. Department of Commerce made an affirmative preliminary determination in the anti-dumping investigation concerning MDI originating from China.
The U.S. Department of Commerce will make a final anti-dumping ruling by January 23, 2026.

On June 16, 2025, India's Directorate General of Trade Remedies under the Ministry of Commerce issued an announcement stating that, upon the application of Garware Hi-Tech Films, an anti-dumping investigation has been initiated on "thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) based surface/paint protection film" products originating from or exported from China.
India has initiated an anti-dumping investigation against Chinese TPU paint protection films, marking the first time the industry has faced such an investigation.

The products involved are "thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) based surface/paint protection films" originating from or exported from China. Paint protection films are typically made from thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC). The anti-dumping investigation specifically targets surface/paint protection films made from TPU.
The product involved is a transparent or colored, flexible polymer film with self-healing properties, applied to the outer surface of craft items or vehicles to protect the surface/paint from scratches, scuffs, road debris, and other forms of damage. As a protective layer, this product can absorb impact and prevent damage to the original paint surface.
The products involved are usually classified under Chapter 39 "Plastics and articles thereof" of the First Schedule to the Customs Tariff Act of 1975 in India. The relevant customs tariff numbers include: 39095000, 39191000, 39199010, 39199090, 39201019, 39201099, 39206190, 39206290, 39206919, 39206922, 39206929, 39206939, 39206999, 39209490, 39209912, 39209919, 39209939, 39209991, 39209999, 39211310, 39211390, 39211900, 39219029, 39219099, 39269069, 39269099. The aforementioned codes are for reference only and do not limit the scope of the investigated products.
The dumping investigation period is from January 1, 2024 to December 31, 2024; the injury investigation period is from April 1, 2021 to December 31, 2024, divided into four phases: April 1, 2021 – March 31, 2022, April 1, 2022 – March 31, 2023, April 1, 2023 – March 31, 2024, and January 1, 2024 to December 31, 2024.
6. The world's largest! The production line for carbon dioxide-based polycarbonate polyols in Anhui has officially commenced operation.

On April 9, 2025, the production launch ceremony for the continuous production facility of carbon dioxide-based new materials by Anhui Pu Carbon New Materials Technology Co., Ltd. was held at the Huainan Modern Coal Chemical Industry Park.
The Anhui 300,000-ton annual production project of carbon dioxide-based polycarbonate polyols is the first set of industrialized production process equipment for this product and technology at a ten-thousand-ton level. The total investment in the project is approximately 2 billion yuan. Once the project is completed and reaches full production capacity, it can effectively fix about 180,000 tons of carbon dioxide, with an estimated annual sales revenue of about 7.5 billion yuan and annual tax revenue of about 300 million yuan, and is expected to create 400 jobs.
The first phase of the project covers an area of 150 acres, with an investment of approximately 600 million yuan, and involves the construction of a production facility with an annual capacity of 50,000 tons of carbon dioxide-based polycarbonate polyol, which is currently the largest carbon dioxide-based polyol facility in the world. Construction commenced in February 2023, and trial production is expected to succeed in January 2025, ushering in a new era of carbon-negative materials in the polyurethane sector with carbon dioxide-based polyols. Once the project reaches full production capacity, it is expected to generate an annual sales revenue of 1.5 billion yuan, with annual taxes amounting to approximately 60 million yuan, and create 150 new jobs. The second phase involves an investment of 1.4 billion yuan, with an annual production capacity of 250,000 tons of carbon dioxide-based polycarbonate polyol and propylene carbonate.
Anhui Pu Carbon New Materials Technology Co., Ltd., established in December 2021, is a high-tech chemical new materials enterprise. The company actively responds to the national "dual carbon" policy, strategically focusing on the technology route and business segment of carbon dioxide-based polyol with a forward-looking perspective. With high-value utilization of carbon dioxide as its core competitive advantage, the company achieves a perfect combination of carbon dioxide utilization and new materials, creating a model of high-value utilization technology of carbon dioxide. The enterprise focuses on the resource utilization of carbon dioxide and actively develops carbon dioxide-based new materials such as polycarbonate polyol (PCE), propylene carbonate (PC), and biodegradable materials (PPC), providing high-performance import substitution products. These materials are widely used in construction, furniture and home decoration, automotive interiors, clothing, insulation, biodegradable materials, new energy, and electronics industries, becoming a key focus of the polyurethane industry for "carbon neutrality" solutions and related technology innovation demonstration projects.

In March 2024, the company's project for an annual production capacity of 300,000 tons of carbon dioxide-based polycarbonate polyols (Phase I) was selected as one of the first batch of "Green Low-Carbon Advanced Technology Demonstration Projects." In August 2024, the National Development and Reform Commission approved the company's special fund subsidy for "Pollution Control and Energy Saving and Emission Reduction" for the carbon dioxide-based polyol project, granting a central budget investment subsidy of 50 million yuan. On December 31, 2024, the company's "Preparation Technology for Carbon Dioxide-Based Polycarbonate Polyether Polyols" was included in the "2024 Green Low-Carbon Product Technology and Supplier Directory" published by the Anhui Provincial Department of Industry and Information Technology.
The environmental impact assessment approval for Wanhua Chemical's 1.5 million tons/year MDI technological transformation and capacity expansion integration project has been granted.

On October 11, 2025, the Fuzhou Ecological and Environmental Bureau issued the approval opinion for the Environmental Impact Report of the 1.5 million tons/year MDI technological transformation and capacity expansion integrated project of Wanhua Chemical (Fujian) Co., Ltd., agreeing to the construction of the project in accordance with the construction site, nature, scale, and environmental protection countermeasures listed in the Environmental Impact Report.
The project is located within the reserved land of the existing plant area of Wanhua Chemical (Fujian) Isocyanate Co., Ltd. in the Jiangyin Port City Economic Zone, Fuzhou. It is planned to upgrade the MDI refrigerant, condensation unit, photochemical unit, and separation unit from the original 800,000 tons/year MDI project to match a production capacity of 1.5 million tons/year MDI. Additionally, relevant utilities and auxiliary facilities will be newly constructed or expanded simultaneously, and the purchase and pre-installation of reaction equipment, towers, heat exchangers, pumps, and other related auxiliary equipment will be carried out. Furthermore, the project will add 700,000 tons/year of MDI, 340,500 tons/year of HCL, and 2,600 tons/year of methanol.
According to the 2024 annual report disclosed by Wanhua Chemical, as of the end of 2024, the company has an MDI production capacity of 3.8 million tons per year. Meanwhile, Wanhua Fujian MDI will undergo technological upgrades and capacity expansion, adding 700,000 tons per year, expected to be completed by the second quarter of 2026. By then, Wanhua's global MDI production capacity will reach 4.5 million tons per year.

On June 13, 2025, Tosoh announced that at the board meeting held on September 26, 2023, the company decided to establish "Tosoh Vietnam Polyurethane Co., Ltd." (hereinafter referred to as "the Vietnamese subsidiary") in Vietnam, and the establishment was officially completed on April 4, 2024. The registered capital of this Vietnamese subsidiary exceeds 10% of the company's registered capital, making it a specific subsidiary of the company. However, it was found that the subsidiary change had not been disclosed in accordance with listing rules prior to this. Although this is a post-factum notification, we sincerely apologize for the omission in disclosure regarding this subsidiary change.

In October 2023, Tosoh announced its plan to construct a methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI) distillation separation facility in Ba Ria-Vung Tau Province, Vietnam. The distillation separation facility will use crude MDI as raw material and produce 100,000 tons of pure MDI and polymeric MDI annually. MDI is a key raw material for the production of polyurethane. Tosoh will import crude MDI from Japan to the distillation separation facility in Vietnam. Therefore, Tosoh plans to establish a wholly-owned subsidiary—Tosoh Vietnam Polyurethane Co., Ltd.
According to the notification, the MDI distillation and separation unit is currently under construction and is expected to be operational in the spring of 2027.

In October 2025, Dow announced that it will permanently close its polyether polyol production facility at the Tertre plant in Belgium by the end of the first quarter of 2026. The plant has a polyether polyol production capacity of 94,000 tons per year.
Last year, Dow announced a strategic review of its European assets, with a particular focus on its polyurethane business. The decision to close its polyether polyols production facility in Tertre, Belgium, is also based on the previous strategic review.
This decision was made against the backdrop of weak demand in the European polyether polyol market, particularly from key end-use sectors such as automotive, appliances, construction, and soft furniture. Overcapacity and the rising volume of imports (with an average annual import volume of 286,000 tons from 2020 to 2024, reaching a record 323,000 tons last year) have further weakened the competitiveness of European producers, with China, South Korea, and Saudi Arabia being the main sources of supply.
The European polyether polyol market is under dual pressure from weak demand and overcapacity, coupled with a continuous increase in imports mainly from Asia, making the industry increasingly difficult. Dow pointed out that high energy costs, a burdensome regulatory environment, and intensifying competitive pressure from imported products (especially from Asia) are key factors in making this decision.
In a letter dated September 29, 2025, Dow informed its customers of this plan. The shutdown will affect 37 official positions and 8 contractor positions. According to the Belgian General Federation of Labor, the polyether polyol production facility is likely to be dismantled after its closure.
Dow emphasizes that customer supply will not be affected and will continue to maintain stable delivery of its existing product portfolio. Dow previously had a production capacity of 530,000 tons/year of polyether polyols in Terneuzen, Netherlands, and an additional capacity of 60,000 tons/year in Tarragona, Spain.
10. Curtain falls! Taiguang China spandex factory decides to shut down and withdraw, laying off over 500 employees.

In August 2025, according to foreign media reports, South Korea's Taekwang Group has decided to completely shut down its Chinese subsidiary, Taekwang Fibers (Changshu) Co., Ltd., marking its total withdrawal from the Chinese market after 20 years. This decision was made due to global market oversupply and weak demand, which led to a cumulative operating loss of 93.5 billion won (approximately 483 million yuan) over the past three years.
On July 31, 2025, South Korea's Taekwang Group announced that its board of directors held a meeting on July 30 and decided to cease operations at Taekwang Chemical Fiber (Changshu) Co., Ltd. The company plans to fully stop production at the factory in August and complete the disposal of inventory sales activities by October. Currently, Taekwang Chemical Fiber (Changshu) Co., Ltd. has 502 employees, and the company plans to collect accounts receivable and lay off all employees by the end of the year.
The board of directors of South Korea's Taekwang Group has decided to raise 100 billion won (approximately 517 million yuan) through a stock issuance to fund its withdrawal from the Chinese market. This funding will be used to repay loans incurred due to accumulated losses and to supplement operational funds. A representative from Taekwang Group stated, "The decision to withdraw from China is a measure to prevent the continued expansion of losses and to strengthen the competitiveness of our core business," and emphasized that "we will enhance operational efficiency based on this decision and accelerate the cultivation of new growth engines."
The Korean Taekwang Group successfully commercialized the production of spandex in South Korea in 1979. During the tenure of Chairman Lee Ho-jin as the representative before 2003, the Taekwang Group established a subsidiary in China and commenced commercial production in 2005, building an overseas spandex production base.
Taiwan Guo Chemical Fiber (Changshu) Co., Ltd. has an annual production capacity of 27,000 tons of spandex. Since its establishment until last year, the cumulative sales amounted to 2.6143 trillion Korean won (approximately 13.558 billion yuan), while the cumulative operating loss reached 68.6 billion Korean won (approximately 356 million yuan). The total operating loss over the past three years has reached 93.5 billion Korean won (approximately 483 million yuan), and in the first quarter of this year alone, the loss was 7.2 billion Korean won (approximately 37.34 million yuan), completely falling into a state of capital impairment.
It is noteworthy that the investment project for Taekwang Group of South Korea to build a second spandex factory in Ningxia, China, has also been suspended.
In 2022, South Korea's Taekwang Group established Taekwang Chemical Fiber (Ningxia) Co., Ltd., planning to construct a differentiated spandex project with an annual output of 108,000 tons. The project plans to invest 4.468 billion RMB and covers an area of 500 acres. The main products include 51,000 tons of 20D spandex, 16,200 tons of 30D spandex, and 40,800 tons of 40D spandex. The project is divided into three phases, each with a spandex production capacity of 36,000 tons. The original plan was to complete the first phase in August 2024, the second phase in August 2025, and the third phase in August 2026. However, in May of last year, Taekwang Chemical Fiber (Ningxia) Co., Ltd. decided to suspend investment and consider previous investment funds as losses, judging them to be unrecoverable.

On March 18, 2025, LyondellBasell and Covestro jointly decided to permanently shut down the propylene oxide/styrene monomer (PO/SM) production unit (PO11) at the Maasvlakte plant in the Netherlands.
PO11 is a 50/50 joint venture that started operations in 2003, utilizing LyondellBasell technology. It has an annual production capacity of 300,000 tons of propylene oxide and 635,000 tons of styrene.
The factory is currently in a shutdown state. It is reported that the operation of the Maasvlakte plant's PO/SM unit will cease in December 2024. The plant was also in a shutdown state last July and has been intermittently closed for years due to economic reasons.
Both companies stated that by the end of 2026, LyondellBasell will implement the procedures for closing the PO/SM plant and preparing for its demolition.
They stated that this decision was made after careful consideration, citing reasons such as global overcapacity, strong growth in imports from Asia, and high production costs in Europe putting continuous pressure on the profitability of the Maasvlakte plant. Unfortunately, this situation is expected to persist, leading to an anticipated lack of long-term profitable production.
Covestro stated that it will continue to supply customers with polyether polyols (the main derivative of propylene oxide) in the European market.

Recently, the 240,000 tons/year polyether polyol (PPG) unit of the Lianhong Gelun integrated project successfully commenced trial production, achieving a smooth full-process operation on the first attempt and producing qualified PPG products, marking a successful "first battle" for the trial production of the Lianhong Gelun integrated project.
The PPG unit is an important component of the Lianhong Gerun integrated project, utilizing domestically developed continuous process technology to produce high-performance PPG products using propylene oxide (PO) and ethylene oxide (EO) as raw materials. It features advantages such as low investment cost, low energy consumption, self-sufficiency in raw materials, high conversion rate, and superior product quality. The products are applied in various fields including home furnishings, automotive, building insulation, textiles, and new energy. The unit provides significant advantages in improving polyurethane foam resilience, compressive permanent deformation, and foam density control. The successful commissioning of the PPG unit will aid the company in further diversifying its product portfolio and enhancing its profitability.

In September 2025, it was reported that INEOS, headquartered in the UK, will indefinitely shut down its production of propylene oxide (PO) and propylene glycol (PG) in Europe, even if its chlorine-based propylene oxide production facility in Germany, with an annual capacity of 210,000 tons, resumes chlorine supply.
On September 8, 2025, INEOS announced to its customers that it would immediately cease the production of propylene oxide and propylene glycol. INEOS will also exit the PO and PG working group of the European Chemical Industry Council (Cefic) in 2026.
The epoxy propane production facility of INEOS located in Cologne, Germany provides raw materials for its nearby propylene glycol production facility with an annual capacity of 120,000 tons. Since a fire at the substation in the Dormagen Chemical Park in Germany on July 12, 2025, which caused a power outage, both facilities have been in a state of shutdown. The fire at the substation also led to Covestro, a German chemical company, announcing on July 15, 2025, that a series of products including chlorine, TDI, and polyols were experiencing force majeure. INEOS announced force majeure for its propylene glycol production on July 18, 2025. INEOS did not announce force majeure for its epoxy propane production, as it is mainly used for internal purposes.
Repair work at the Dormagen chemical park in Germany is underway, but the damage is severe, and full operational recovery is not expected before the first quarter of 2026. However, INEOS has informed customers that it will not resume production of propylene oxide and propylene glycol. This decision may have been made prior to the fire at the Dormagen chemical park in Germany in July, as some downstream users of INEOS propylene oxide have been seeking alternative sources since at least mid-second quarter.
In a letter to customers dated September 8, 2025, INEOS mentioned: "The high costs of raw materials, natural gas, and energy, combined with an oversupply in the propylene oxide market and weak local demand for derivatives, put Europe at a significant disadvantage compared to other regions. Furthermore, the competitive disadvantage of the chlorohydrin process for producing propylene oxide, compared to more efficient processes, further hinders our ability to justify production continuity."

On June 29, 2025, Binhua Group's "Calcium Saponification Process for Epoxy Propylene via Chlorohydrin Method" successfully passed the expert acceptance organized by the China Chlor-Alkali Industry Association, becoming the first domestic enterprise to be verified for the production of epoxy propylene using the chlorohydrin method.
In recent years, the Chinese government has emphasized green development in the chlor-alkali chemical industry, mainly due to the severe environmental pollution caused by low-end production capacity in the propylene oxide industry. As a result, the pace of eliminating low-end production capacity both globally and domestically has been accelerating. The National Development and Reform Commission has announced the "Industrial Structure Adjustment Guidance Catalog (2024 Edition)" (referred to as the "Catalog"), which explicitly lists the chlorohydrin production process as a restricted category. It mandates that starting from December 31, 2025, except for facilities meeting specific conditions (fresh water usage not exceeding 15 tons per ton of product and waste residue generation not exceeding 100 kilograms), all others will face mandatory elimination. This indicates that a large amount of domestic production capacity will face serious elimination risks.
At the same time, the propylene oxide industry is also deeply trapped in a supply surplus dilemma. Data shows that in 2024, China's propylene oxide production capacity will rise to 7.47 million tons per year, an increase of about 23.7% compared to 6.12 million tons per year in 2023. Among this, the chlorohydrin process capacity is about 2 million tons, accounting for approximately 28%. In stark contrast, the annual demand in the industry remains stable at around 5 million tons, highlighting the problem of overcapacity. Against this backdrop, the elimination of outdated production capacity has become urgent, while enterprises willing to innovate and break through will find development opportunities amidst the wave of industry transformation.
Faced with industry transformation, Binhua Group chose to break through from the technology side, leveraging its circular economy industrial chain advantages to form a special R&D team composed of technical experts from various fields such as process, production, and equipment. The team innovatively constructed a coupled development path of "source reduction-process efficiency enhancement" and carried out comprehensive upgrades and modifications to the propylene oxide plant.
Through technological breakthroughs, Binhua Group has successfully reduced the fresh water usage per unit product to below 10 tons and the waste residue generation to below 95 kilograms, significantly lowering the standards set by the national "Directory," which stipulates 15 tons of fresh water usage and 100 kilograms of waste residue generation. This major technological breakthrough not only achieved the national policy requirements six months ahead of schedule but also realized dual breakthroughs in the innovation of recycled water resource utilization technology and energy-saving carbon reduction of the equipment.
The expert group from the China Chlor-Alkali Industry Association conducted a comprehensive and in-depth assessment of the technological advancement and environmental friendliness of BinHua's propylene oxide industrial circular economy system through discussions and on-site inspections. The expert group gave high praise to the process, especially noting that "the BinHua Group model has pioneered a new path for the deep integration of the chlorohydrin method for propylene oxide and calcium method saponification process with circular economy, providing a replicable and promotable practical solution for the industry's green transformation."
With this technological upgrade, Binhua Co., Ltd. is expected to successfully meet the production requirements for propylene oxide using the chlorohydrin method outlined in the "Directory" and avoid the risk of capacity elimination. While other companies in the industry are still concerned about the retention or elimination of capacity, Binhua Co., Ltd. has taken the lead in completing the technological positioning, standing out in the competition on the supply side.
15. The world's largest bio-based BDO plant has been put into operation! It will supply BASF and Lycra company for the long term.

On July 11, 2025, it was announced that Qore, a joint venture between Cargill and HELM, has officially launched its biobased 1,4-butanediol (BDO) plant. Located in Eddyville, Iowa, USA, the plant represents a total investment of $300 million and has an annual production capacity of 65,000 tons of biobased BDO (brand name QIRA®), recognized as the world's largest biobased BDO production facility.
The commissioning of this plant marks a significant milestone in sustainable chemical manufacturing. Qore was established with the aim of supporting major consumer brands in transitioning from fossil-based chemical ingredients to renewable bio-based alternatives.
The bio-based BDO plant utilizes Geno's proprietary biocatalyst and fermentation technology, using plant sugars derived from locally grown dent corn (industrial corn) in the United States as raw materials, to produce bio-based BDO through a one-step direct fermentation process.
Geno is a pioneer in the field of industrial biotechnology, having invented, expanded, and designed the GENO™ Bio-BDO process, which has now been licensed to industrial producers worldwide. Compared to traditional fossil-based BDO production processes, this process is expected to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 90%. The process was initially commercialized in 2016 with the launch of the first licensed plant.
The GENO™ Bio-BDO process has been licensed to three large commercial plants.
The first company: Novamont is located in Italy, with a production plant that has a bio-based BDO capacity of 30,000 tons per year. The company is also independently researching and developing technology processes to produce bio-based BDO using non-food crops like cardoon as raw materials. Novamont primarily uses bio-based BDO to produce PBAT (brand name Origo-Bi®), and its blend with starch is known as Mater-Bi®, which has been rapidly developing in fields such as biodegradable plastic bags.
The second company: Qore, a joint venture between Cargill and HELM, has launched a factory located in the United States with an annual production capacity of 66,000 tons of bio-based BDO (brand name QIRA®).
In September 2022, Lycra Company and Qore announced a partnership to produce bio-based LYCRA® fiber using bio-based BDO (QIRA®). This bio-based spandex fiber is set to be launched on a large scale in early 2025, becoming the world's first large-scale supply of bio-based spandex fiber.
In May 2024, LYCRA Company signed a letter of intent with Dalian Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. (referred to as "Dalian Chemical") to convert the QIRA® brand bio-based BDO into low-carbon and environmentally friendly PTMEG. This is the main component of the patented bio-based LYCRA® fiber. This unique PTMEG will enable the renewable content of LYCRA® fiber to reach 70% of the fiber content. Dalian Chemical will also become the world's first company to produce this low-carbon, environmentally friendly bio-based PTMEG on a large scale.
In September 2023, BASF announced an agreement with Qore to secure a long-term supply of bio-based BDO (QIRA®). With bio-based BDO, BASF will expand its existing portfolio of butanediol derivatives, such as bio-based specifications of polytetrahydrofuran (PolyTHF) and tetrahydrofuran (THF).
In 2024, Hyosung TNC, the textile division of South Korea's Hyosung Group, obtained a technology license for the GENO™ Bio-BDO process. In April 2024, during the "Ba Ria-Vung Tau Province Vision Declaration and Investment Approval Ceremony" held at the Phu My 2 Industrial Park in southern Vietnam, Hyosung TNC received investment approval from the Ba Ria-Vung Tau provincial government for the "Hyosung BDO Project." Hyosung TNC plans to invest $1 billion to build a bio-based BDO plant in Vietnam with an annual production capacity of 200,000 tons. Geno's mature technology enables Hyosung TNC to rapidly advance its project, and it is expected to achieve an annual production and sale of 50,000 tons of bio-based BDO in the first half of 2026. On the raw material side, the plant innovatively uses sugarcane fermentation technology, replacing traditional coal and other fossil materials with environmentally friendly sugarcane extracts to produce bio-based BDO.
Once the factory is completed and put into operation, Xiaoxing Tianxi will establish the largest bio-based spandex factory in Vietnam. Notably, this will be the world's first vertically integrated production system for bio-based spandex, achieving a complete process from raw materials to fibers. Xiaoxing Tianxi will produce bio-based BDO at the factory located in the southern Ba Ria-Vung Tau Province, produce PTMEG at a nearby factory in Dong Nai Province, south of Ho Chi Minh City, and then use it to mass-produce regen™ BIO spandex at the Dong Nai spandex factory.

On April 30, 2025, Dongsung Chemical announced the grand opening of its new polyurethane (PU) production plant located in Karawang, Indonesia.
The completion ceremony of the factory attracted over 200 guests, including important leaders and dignitaries from South Korea and Indonesia. The attendees included Baek Jeong-Ho, Chairman of Dong Sung Chemical, Co-CEOs Baek Jin-Woo and Lee Man-Woo, Rosan Perkasa Roeslani, the Indonesian Minister of Investment and Downstream Industry, and Park Su-Deok, the South Korean Ambassador to Indonesia.
It is reported that the polyurethane plant started construction in September 2023, completed trial production in early 2025, and began full production in February 2025.
The new factory covers an area of 81,000 square meters and has an annual production capacity of 67,000 tons of prepolymers, polyester polyols, and polyurethane resins, which is three times the output of Dongcheng Chemical's existing polyurethane plants in South Korea, Vietnam, and China. The projected annual revenue is approximately $150 million.
The factory is also equipped with a polyurethane base material storage capacity of up to 1000 tons, ensuring supply chain stability and uninterrupted production even in the event of global supply disruptions. The advanced automation system further enhances operational efficiency and product quality.
The factory is located in an important industrial park in Indonesia and will become the strategic base for Dongcheng Chemical's global expansion, especially in the Southeast Asian, American, and European markets. In addition to its existing footwear, synthetic leather, automotive, and electronics businesses, the company also plans to enter the furniture materials market.

On April 21, 2025, Sun Yat-sen University signed a contract with Zhuhai Zhongguan Petrochemical Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as "Zhuhai Zhongguan") for the "Carbon Dioxide-Based Polycarbonate Diol Synthesis Technology Achievement Transformation Project" at Sun Yat-sen University.
According to the agreement, Sun Yat-sen University licenses the relevant patent technology for the synthesis of carbon dioxide-based polycarbonate diols to Zhuhai Zhongguan. Both parties will jointly tackle the scaled-up industrial technology for the synthesis of carbon dioxide-based polycarbonate diols, with the expectation of establishing an industrial production line in Zhuhai Zhongguan with an annual output of 300,000 tons and an estimated output value exceeding 5 billion RMB.
Carbon dioxide-based polycarbonate diol is a novel and important low molecular weight diol material. The carbon dioxide consumption per ton of carbon dioxide-based polycarbonate diol product is close to 50%, resulting in extremely low production costs. Carbon dioxide-based polycarbonate diol is an important raw material for synthesizing polyurethane. Compared to polyether diols and polyester diols, polyurethane materials synthesized with polycarbonate diols possess excellent weather resistance and mechanical properties. Carbon dioxide-based polycarbonate diol has a wide range of applications in elastomers, coatings, adhesives, and paving materials.

Asahi Kasei Fine Chemicals (Nantong) Co., Ltd. has completed its relocation within the Nantong Economic and Technological Development Zone, with the completion ceremony held on March 7, 2025. The first phase of the new plant is ready for operation, and commercial operations will sequentially commence at the end of March, injecting strong momentum into the high-performance polyurethane industry.
Asahi Kasei actively responds to the guidelines provided by the "Yangtze River Protection Law of the People's Republic of China" and related regulations, relocating its original factory to the southern area of the same development zone.
In the future, we will actively expand high-performance products that can respond to environmental policies such as VOC reduction. This factory relocation also demonstrates Asahi Kasei's strategic importance placed on the Chinese market.
The factory has been producing high-performance polyurethane resin raw material HDI-based polyisocyanate "Desmodur™" for coatings since 2007, and has been producing polyurethane resin raw material polycarbonate diol "Desmophen™" since 2014.
Duromide™ HDI Polyisocyanate: A high-quality HDI type non-yellowing curing agent with excellent weather resistance and mechanical properties, widely applicable in coatings, inks, adhesives, and other fields. Duromide™ can significantly enhance the performance of coatings, making them less prone to corrosion and yellowing when used in industrial anti-corrosion paints.
Duonal™ Polycarbonate Diol: As a polyurethane raw material PCD, it can be used in coatings, synthetic leather, elastomers, and other fields. It can maintain a soft and comfortable touch for a long time and is durable, commonly used for coatings in automotive interiors and high-end furniture. Synthetic leather used in automotive interiors can provide premium appearance and touch.

On November 21, 2025, Longhua New Materials announced the completion and production of the expansion project for an annual output of 330,000 tons of polyether polyols.
On January 3, 2025, Longhua New Materials disclosed the announcement titled "Announcement on the Acquisition of Project Filing by Shandong Longhua New Materials Co., Ltd." (Announcement No.: 2025-002). In order to enhance the company's profitability, risk resistance capability, and overall competitiveness, the company plans to carry out an expansion project for the annual production of 330,000 tons of polyether polyol within the existing plant area, with an estimated total investment of 150 million yuan.
The company's investment in the expansion project of an annual output of 330,000 tons of polyether polyol has been fully completed. The trial production has passed expert evaluation and has been filed with the Gaoqing County Emergency Management Bureau, meeting the conditions for trial production. The expansion project with an annual output of 330,000 tons of polyether polyol has officially entered the trial production stage, and on November 20, 2025, qualified products were successfully produced. All product indicators met the premium grade, achieving a successful startup in one go.
The project aims to construct a production capacity of 330,000 tons per year for polyether polyols. The main products include high-activity soft foam polyether polyols and CASE (Coatings, Adhesives, Sealants, and Elastomers) polyether polyols, primarily used in automotive, footwear, apparel, adhesives, and foaming agents. Particularly in the automotive sector, with the rapid global development of the new energy vehicle industry and national policies to expand domestic demand and implement car replacement subsidies, the company has established stable cooperative relationships with numerous well-known automobile manufacturers or component and accessory suppliers. This is due to the products' strong support in downstream applications, excellent comfort, uniform and delicate pores, fast curing speed, tear strength, and environmental safety advantages. These products are applied in Mercedes-Benz, BMW, SAIC, BYD, Great Wall, Chery, Geely, GAC, Dongfeng, Changan, as well as Tesla, Li Auto, and XPeng. After the project is put into operation, the company's total production capacity for the polyether series will reach 1.29 million tons per year, further consolidating its market position in the domestic polyether sector. The implementation of this project will enhance the company's profitability, risk resistance, and overall competitiveness, aligning with the company's long-term strategic plan to delve into the new materials field and serving the interests of the company and all shareholders.

On the evening of July 27, 2025, an odor alarm was reported in Omuta City, Fukuoka Prefecture, Japan. A chlorine leak occurred at Mitsui Chemicals' facility located at 30 Asamuta-machi, Omuta City, Fukuoka Prefecture, within the company's polyurethane production department's isocyanate division TDI unit.
Mitsui Chemicals' Omuta plant reported that on July 27, 2025, at 17:31, a detector near the TDI unit's degassing tower triggered an alarm, confirming a chlorine gas leak. The plant immediately ceased operations, and by 23:39 that evening, it was confirmed that there were no gas or odor leaks around the plant.
On July 27, 2025, the traditional summer festival "Omuta Daija Yama Festival" was being held in Omuta City, Fukuoka Prefecture, Japan, with related activities taking place near the site of a chlorine leak incident. Due to the impact of the chlorine leak, some activities of the festival were forced to be canceled midway.
According to Mitsui Chemicals, a total of 234 people sought medical attention due to feeling unwell (as of August 27, including those who returned for follow-up visits). Among them, 17 individuals were hospitalized for observation and treatment (all have been discharged).
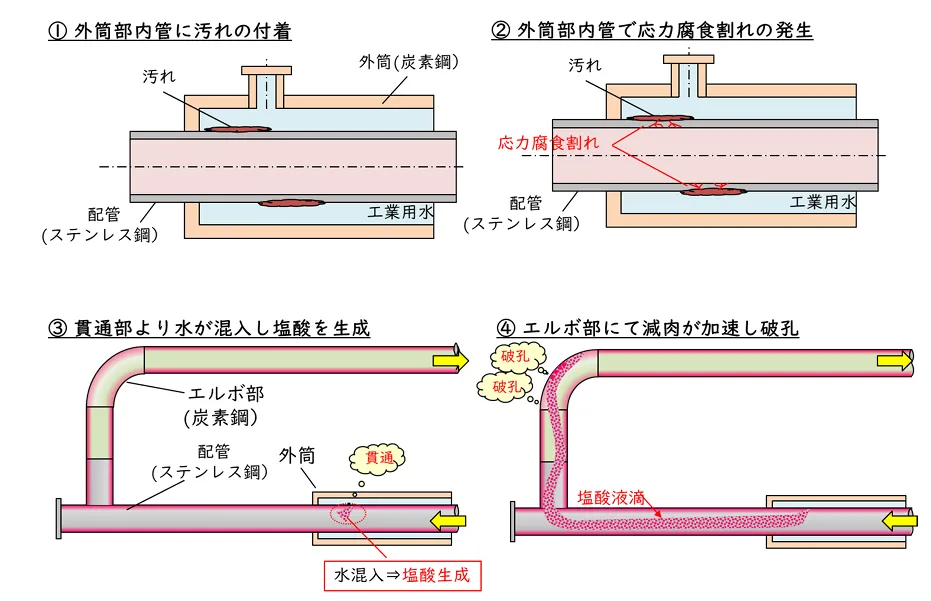
The cause of the accident was the rupture of the exhaust pipe at the top of the de-gassing tower in the TDI unit. It is reported that the outer tube cooling device located above the rupture site of the exhaust pipe (double-pipe structure: the outer pipe is filled with industrial water, and the inner pipe is filled with process gas) had dirt attached to the surface of the inner stainless steel pipe (the side in contact with industrial water), resulting in stress corrosion cracks. Industrial water seeped into the process gas side from these stress corrosion cracks and reacted with chlorine-based gases to form hydrochloric acid. The hydrochloric acid droplets came into contact with the elbow of the exhaust pipe at the top of the tower and surrounding areas, accelerating the thinning of the pipe wall, ultimately leading to a rupture.
【Copyright and Disclaimer】The above information is collected and organized by PlastMatch. The copyright belongs to the original author. This article is reprinted for the purpose of providing more information, and it does not imply that PlastMatch endorses the views expressed in the article or guarantees its accuracy. If there are any errors in the source attribution or if your legitimate rights have been infringed, please contact us, and we will promptly correct or remove the content. If other media, websites, or individuals use the aforementioned content, they must clearly indicate the original source and origin of the work and assume legal responsibility on their own.
Most Popular
-

Clariant Unveils Cost-Cutting Plan Details, Plans to Shut Down Multiple Plants
-

Dow, Wanhua, Huntsman Intensively Raise Prices! Who Controls the Global MDI Prices?
-

[Today's Plastics Market] General Materials Weakly Fluctuate, Engineering Materials Steadily Rise
-

U.S. Appeals Court Officially Rules: Trump Tariff Unlawful and Void!
-

Daily Review: Polyethylene Prices Under Weak Consolidation, Sellers Face Significant Pressure to Move Inventory






