Chinese team develops new method for biodegradable pu plastics, achieving over 10-fold efficiency increase
On July 19, Xinhua News reported that a research team in China has recently discovered a new method for the biodegradation of PU (polyurethane) plastic.It can increase the degradation efficiency by more than 10 times.。
According to reports, the research team from the Structural Biology Platform Laboratory of the Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, has "decoded" a PU plastic depolymerase: they obtained the crystal structure of this wild-type enzyme from nature, thereby revealing the molecular mechanism by which the enzyme can efficiently degrade PU plastic.
Based on this, the research team combined evolutionary-guided enzyme mining techniques to not only find a new wild-type PU depolymerase but also optimized its structure and made molecular modifications.Developed a double mutant with significantly improved performance.Some mutants of this "artificial enzyme" have an degradation efficiency for polyester polyurethane that is nearly 11 times higher than that of the wild-type enzyme, significantly improving the recycling rate of PU plastics.

IT Home has reported that the biological method is an international hotspot in the research of waste plastic degradation technology. Compared to the commonly used "high temperature and high pressure" physical methods and "high salt and strong acid" chemical methods, the biological method uses enzymes as degradation tools, taking advantage of their ability to accelerate chemical reactions, to “eat” plastic in a low-energy, low-pollution manner.
In addition to the above advantages,Biological methods can achieve multiple "cycles" of plastic degradation.Researcher Liu Weidong from the Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, introduced that after biodegradation by biological enzymes, waste plastics will be transformed into various monomeric small molecules that make up plastics. Not only can these small molecules be directly used for plastic regeneration, but the depolymerizing enzymes can also continue to be used for plastic degradation before they become inactive. "This makes the biodegradation of waste plastics a typical example of a circular economy."
It is reported that PU plastic is very common in people's daily lives.Thermal insulation foam boxes and sponges in car seat cushions are all made from it.Compared to the relatively mature and single chemical bond of PET plastics in biodegradation, PU plastics have more chemical bonds, making biodegradation more difficult, and fewer PU depolymerases have been discovered.
The United Nations Environment Programme data shows that,Currently, humans produce over 400 million tons of plastic each year, of which less than 10% is recycled.。
Liu Weidong believes that this achievement provides a more efficient tool for the large-scale biological recycling of PU plastics and offers a new solution for the recycling of degraded plastic waste. "Next, we will promote the industrial application of enzyme preparations."
【Copyright and Disclaimer】The above information is collected and organized by PlastMatch. The copyright belongs to the original author. This article is reprinted for the purpose of providing more information, and it does not imply that PlastMatch endorses the views expressed in the article or guarantees its accuracy. If there are any errors in the source attribution or if your legitimate rights have been infringed, please contact us, and we will promptly correct or remove the content. If other media, websites, or individuals use the aforementioned content, they must clearly indicate the original source and origin of the work and assume legal responsibility on their own.
Most Popular
-

Overseas Highlights: PPG Establishes New Aerospace Coatings Plant in the US, Yizumi Turkey Company Officially Opens! Pepsi Adjusts Plastic Packaging Goals
-
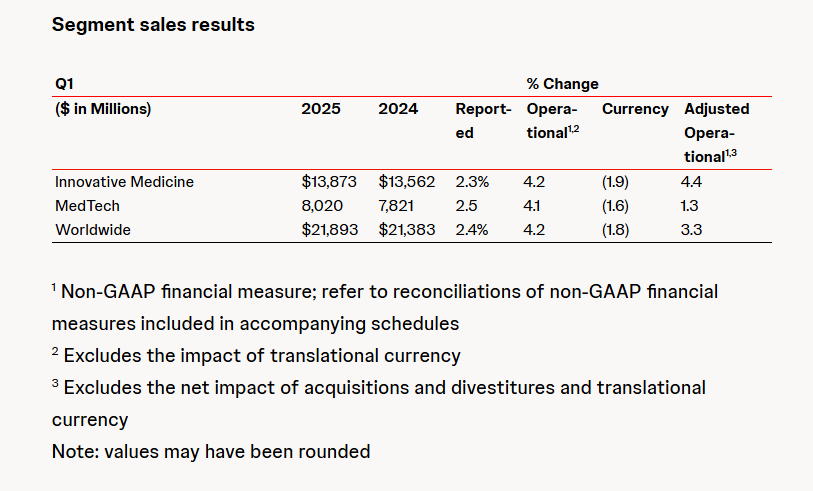
Abbott and Johnson & Johnson: Global Medical Device Giants' Robust Performance and Strategies Amid Tariff Pressures
-

BYD releases 2024 ESG report: Paid taxes of 51 billion yuan, higher than its net profit for the year.
-

Behind pop mart's surging performance: The Plastics Industry Embraces a Revolution of High-End and Green Transformation
-
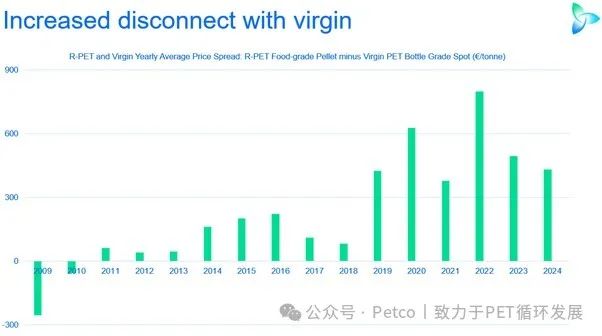
The price difference between recycled and virgin PET has led brands to be cautious in their procurement, even settling for the minimum requirements.



