Volkswagen's passat production plant to close as it enters deep water of transformation in china

Recently, there have been reports in the industry that the Volkswagen Group (referred to as "Volkswagen") and its Chinese partner SAIC Motor Corporation will close their joint venture factory in Nanjing. Production at the factory has already halted, and it is expected to gradually close down in the second half of the year.
On July 15, the Economic Observer consulted Volkswagen China about the news of the closure of the Nanjing factory. The response stated: "SAIC Volkswagen continues to deepen and implement the 'In China, For China' strategy, working together with both shareholders to accelerate the transition to the era of electrification and intelligent connected vehicles. As part of this strategic implementation, SAIC Volkswagen is making corresponding adjustments to its production capacity and optimizing its production network layout."
SAIC Volkswagen's Nanjing plant was established in 2008 and is a key step for SAIC Volkswagen to expand its production capacity in China. In April 2008, then-CEO of Volkswagen Martin Winterkorn and then-chairman of SAIC Group Hu Maoyuan jointly inaugurated the Shanghai Volkswagen (the predecessor of SAIC Volkswagen) Nanjing plant.
"The closure of the fuel vehicle factory in Nanjing is a 'self-harming move' for Volkswagen, and it also marks the beginning of its electric transformation entering the 'deep water zone'," said Bai Wenxi, vice chairman of the China Enterprise Capital Alliance, to the Economic Observer.
The economic account behind the shutdown
SAIC Volkswagen's Nanjing factory was formerly the Nanjing Fiat factory under the original Nanjing Automobile Group. After SAIC acquired Nanjing Automobile in 2007, Shanghai Volkswagen urgently needed to expand production due to a surge in sales, while Nanjing Automobile's factory was idle due to Fiat's withdrawal. Ultimately, SAIC transformed the Nanjing Fiat factory into Shanghai Volkswagen's first production base outside of Shanghai.
In April 2008, the Shanghai Volkswagen Nanjing plant was completed and put into production, utilizing production lines that meet German standards, and it produced tens of thousands of Santanas in that year. In the 2010s, the Nanjing plant became the "cradle" of the mid-to-high-end sedan, the Passat. From 2015 to 2018, SAIC Volkswagen, relying on hot-selling models like the Passat, repeatedly claimed the title of the top-selling passenger car manufacturer in the country.
The Nanjing factory is the first complete vehicle factory that Volkswagen has fully closed in China. In 2022, SAIC Volkswagen's Shanghai Anting No. 1 plant partially shut down, transferring fuel vehicle production to the Yizheng factory, with the original site converted into a research and development center. In 2024, for economic reasons, SAIC Volkswagen plans to sell the Xinjiang factory to external parties.
The upgraded and transformed SAIC Volkswagen Jiangsu base is located in the Yizheng Economic Development Zone of Jiangsu Province. Within the park, there are more than 100 parts manufacturers, forming a trillion-yuan industrial cluster that includes key components such as automotive interior and exterior trim, automotive powertrains, high-end automotive electronics, automotive safety systems, and the automotive aftermarket. Benefiting from the in-depth promotion of the Yangtze River Delta integration development strategy, the Yizheng Economic Development Zone, with its superior geographical location and policy support, has integrated into the Yangtze River Delta automotive industry cluster, an insider from SAIC Volkswagen told the Economic Observer.
Bai Wenxi stated that the reason Volkswagen closed its factory in Nanjing is partly due to the fact that the market segment for the Passat produced at the Nanjing factory has been rapidly encroached upon by domestic electric vehicle models such as the BYD Han, NIO ET5, and Xpeng P7. By 2024, the production capacity utilization rate of SAIC Volkswagen had dropped to 55%. On the other hand, the Nanjing factory is located in the core area of the Jiangning Development Zone, which has logistical constraints and limited space.
Volkswagen's "In China, for China" strategy requires it to focus resources on the development of localized electric vehicle platforms and regional electronic and electrical architecture research centers. The cost of transforming the old ICE production line at the Nanjing factory is high, and the returns are limited, said An Guangyong, an expert from the All-China Federation of Industry and Commerce's Mergers and Acquisitions Credit Management Committee, in an interview with the Economic Observer.
According to official information from SAIC Volkswagen, the Nanjing factory produces the Volkswagen brand Passat, as well as the Skoda brand Superb and Kamiq. Skoda was established in 1895, acquired by Volkswagen in 1991, and introduced to the Chinese market by Shanghai Volkswagen in 2005.
In the Chinese market, the Skoda brand is seen as a cost-effective alternative to the Volkswagen brand and was once very popular among consumers. In recent years, as the penetration rate of new energy vehicles in the domestic auto market continues to rise, and the market share of domestic brands keeps increasing, Skoda's sales have been declining. In 2024, Skoda delivered only 17,500 vehicles in China, a year-on-year decrease of 23.1%, representing a reduction of over 90% compared to the peak sales of 341,000 vehicles in 2018.
"Volkswagen's production capacity in China is close to 5 million vehicles, but the actual output in 2024 will be less than 3 million vehicles. Closing 360,000 units of inefficient capacity can clear fixed costs and labor burdens in one go," said Berndt W. H.
The trade-offs of electrification transformation
In An Guangyong's view, Volkswagen's closure of its Nanjing factory is a strategic move in its global electrification transition. Under the influence of factors such as a sharp shift in demand, intensified price wars in electric vehicles, and adverse macroeconomic conditions, this action by Volkswagen can be seen as a necessary pain for the "turning of the elephant," and not a sign of pessimism towards the Chinese market.
According to an insider from SAIC Volkswagen, the company has been adopting a "one-time planning, step-by-step implementation" approach since 2015, with the Shanghai base taking the lead. Several factories have completed or are in the process of transitioning to electric vehicle production. Recently, the Jiangsu base has also undergone corresponding resource integration and upgrading to support the implementation of future product strategies and further enhance operational efficiency.
In recent years, the global automotive industry's transition to electrification has faced numerous ups and downs, and there has even been a resurgence of gasoline vehicles. However, Volkswagen is one of the multinational car companies with the most resolute attitude towards electrification. "Volkswagen firmly believes that electrification is the future of mobility," said CEO Oliver Blume in 2024.
According to the official plan, from 2025 to 2029, Volkswagen intends to keep its investment scale within 170 billion euros, with funding primarily allocated to new products, regional markets, battery business, pure electric vehicle platforms, and advanced fuel vehicles with ongoing hybridization. By 2030, Volkswagen plans to launch 30 pure electric vehicle models.
In the first half of this year, Volkswagen's global deliveries of pure electric vehicles reached 465,500 units, an increase of 47% year-on-year, with a growth rate of about 90% in the European market. Currently, one-fifth of the vehicles delivered by Volkswagen in the Western European market are pure electric vehicles, and the corresponding order volume has increased by over 60%. Amidst the rapid growth in pure electric vehicle sales, Volkswagen's total global vehicle deliveries reached 2.13 million units in the first half of the year, achieving a year-on-year growth of 1.4%.
"We are continuously advancing our electrification transformation through a highly attractive product portfolio," said Marco Schubert, a member of the board responsible for sales at the Volkswagen Group. "The order volume for pure electric models has increased by over 60% year-on-year, which gives us confidence in the development for the second half of the year."
However, Volkswagen still faces profit pressure. According to the financial report, in the first quarter of this year, Volkswagen Group's sales revenue was 77.6 billion euros, a year-on-year increase of 2.8%; operating profit was 2.9 billion euros, a significant decline compared to 4.6 billion euros in the same period last year. Regarding the profit decline, Volkswagen attributed part of the reason to tariff factors. It is understood that due to the uncertainty of U.S. tariffs, Volkswagen has suspended the transportation of cars from Mexico by rail and will temporarily hold cars transported from Europe at ports.
In addition, the challenges in the Chinese market cannot be ignored by Volkswagen. In the first half of this year, Volkswagen's delivery volume in the Chinese market was 1.31 million vehicles, a year-on-year decrease of 7.1%, with the delivery volume of pure electric vehicles declining by more than 30% year-on-year.
Not only for the general public, but also for major multinational automakers that are advancing their electrification transformation, China is one of the most challenging markets. In China, from new car manufacturers like NIO, Xiaopeng, and Li Auto, to leading domestic companies like Geely and BYD, and even cross-border giants like Xiaomi, local new energy vehicle companies have gained first-mover advantages after years of fierce competition in the domestic market. It is not easy for multinational car companies to establish a foothold in the Chinese new energy vehicle market.
"The direction of Volkswagen's electrification transformation is correct, but the pace in the Chinese market is still relatively slow," said Berndt. He believes that 2025 to 2026 is Volkswagen's "last window period" in China. If new products cannot quickly catch up with the leading new forces in China in terms of cost, intelligence, and channels, its market share will continue to be eroded.
New chips in the Chinese market
"The public needs to 'accelerate again' in China. The closure of the Nanjing factory indicates that Volkswagen has abandoned the transitional model of 'using fuel vehicles to support electric vehicles' and is entering the second phase of 'shut down and transition, concentrating resources.' The collaboration with Xpeng, the introduction of the MEB-Plus platform, and the implementation of unified battery cells are all visible new assets for Volkswagen's future," said Bernd W. Becher.
In July 2021, Volkswagen Anhui and Guoxuan High-Tech reached an agreement for Guoxuan High-Tech to develop a new generation of standard battery cells for Volkswagen's electric vehicles in China. According to Volkswagen's plan, the standard battery cells will significantly reduce battery cell costs by adopting a unified design standard. In September 2024, Guoxuan High-Tech revealed in response to investor inquiries that the Volkswagen standard battery cell factory has the production capability, and the delivery time will be determined based on the production progress and demand of Volkswagen's vehicles.
In 2023, Volkswagen invested approximately $700 million to acquire a 4.99% stake in Chinese electric vehicle startup Xiaopeng Motors. In July 2024, Volkswagen and Xiaopeng Motors signed a joint development agreement for the electronic and electrical architecture technology cooperation, aimed at jointly developing the electronic and electrical architecture for Volkswagen's CMP and MEB platforms produced in China. According to the plans of both parties, starting in 2026, all domestically produced Volkswagen brand models based on the CMP and MEB platforms will be equipped with this electronic and electrical architecture.
The Economic Observer has learned from Volkswagen China that starting in the second half of this year, Volkswagen's next-generation intelligent connected vehicle products are scheduled to be delivered to Chinese customers. By 2026, Volkswagen plans to launch over 20 new intelligent connected models in China, covering various powertrains including gasoline, pure electric, plug-in hybrid, and extended-range vehicles.
Recently, the Volkswagen Supervisory Board held a meeting and renewed the contract of the Group's Board members and China region head, Berndt, for an additional three years, until the summer of 2028. "This early renewal reflects the Supervisory Board's recognition of the rapid advancement and achievements of the China strategy, and sends a strong signal to the Group internally and to our Chinese partners: the Volkswagen Group will fully support the transformation direction of the China region and continue to deepen our local presence," the Volkswagen Group stated.
An Guangyong stated that Volkswagen's transformation in the Chinese market is effectively accelerating, but the challenges posed by the external environment cannot be overlooked. "In the past 18 months, the average price of electric vehicles in China has dropped by over 25%, and the ongoing price war is continually compressing profit margins. Geopolitical factors and U.S. semiconductor export controls, which restrict high-performance chips and cross-border data, will also increase supply chain and compliance costs," he said.
【Copyright and Disclaimer】The above information is collected and organized by PlastMatch. The copyright belongs to the original author. This article is reprinted for the purpose of providing more information, and it does not imply that PlastMatch endorses the views expressed in the article or guarantees its accuracy. If there are any errors in the source attribution or if your legitimate rights have been infringed, please contact us, and we will promptly correct or remove the content. If other media, websites, or individuals use the aforementioned content, they must clearly indicate the original source and origin of the work and assume legal responsibility on their own.
Most Popular
-
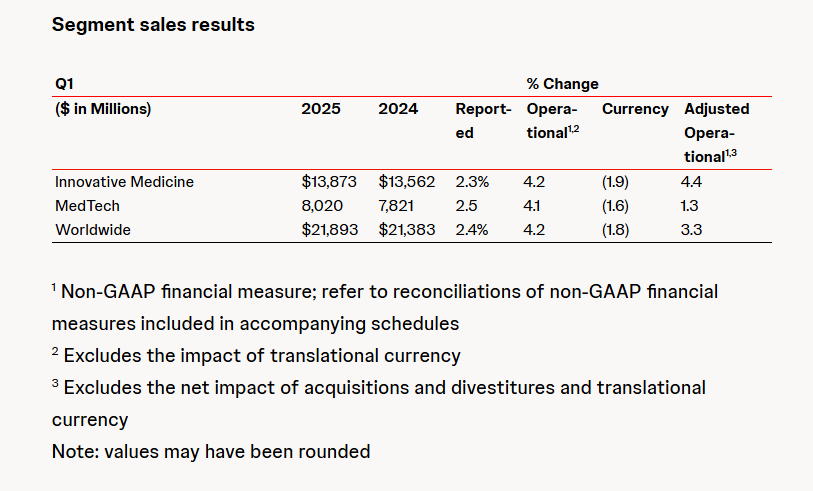
Abbott and Johnson & Johnson: Global Medical Device Giants' Robust Performance and Strategies Amid Tariff Pressures
-

Overseas Highlights: PPG Establishes New Aerospace Coatings Plant in the US, Yizumi Turkey Company Officially Opens! Pepsi Adjusts Plastic Packaging Goals
-

BYD releases 2024 ESG report: Paid taxes of 51 billion yuan, higher than its net profit for the year.
-
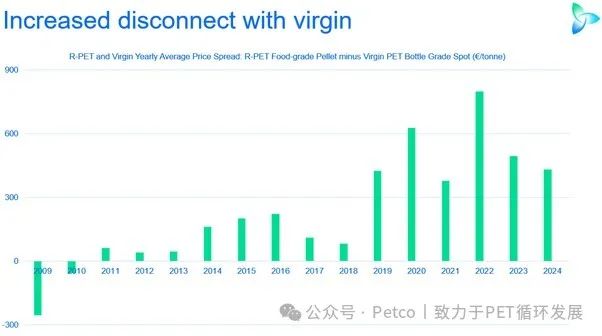
The price difference between recycled and virgin PET has led brands to be cautious in their procurement, even settling for the minimum requirements.
-

Which brand of AI TV is good? Samsung Vision AI interprets the new industry standard with its "technical advantage."



