Completely based on the recycling of post-industrial and post-consumer textile waste, BASF's first loopamid plant is commercialized.
On March 27, BASF announced the commissioning of the world's first commercial Loopamid plant. The production facility located at the Caojing site in Shanghai, China, has an annual capacity of 500 metric tons, marking an important step toward sustainable product supply in the textile industry. "The launch of this facility once again demonstrates BASF's innovative strength," said Dr. Stephan Kothrade, Member of the Board of Executive Directors and Chief Technology Officer of BASF. "As an integral part of our strategy, we use chemistry to develop solutions that address the biggest challenges of our time. Loopamid transforms textile waste into valuable resources, helping to conserve raw materials and close the loop in the textile cycle."
Loopamid is a recycled polyamide 6 entirely based on textile waste. The new production facility supports the textile industry's growing demand for sustainable polyamide 6 fibers. "I am proud of our team, who have worked with great enthusiasm and dedication to bring loopamid to commercialization," said Ramkumar Dhruva, President of BASF's Monomers business unit. "The technology behind loopamid allows for textile-to-textile recycling of polyamide 6 in various fabric blends, including those mixed with elastic fibers. I believe loopamid not only makes a significant contribution to the textile circular economy but also helps our customers achieve their sustainability goals."
Factory and Loopamid product GRS certification

The new Loopamid factory integrated into the Shanghai Caojing Polyamide-6 plant.
The production quantities of both the factory and Loopamid are in accordance with the Global Recycle Standard (GRS). This certification assures consumers and textile manufacturers that Loopamid is made from recycled materials and that the production process meets specific environmental and social standards. Additionally, the first yarn manufacturers are successfully using Loopamid.
Industrial and consumer textile waste
As the foundation of loopamid
To produce Loopamid in the new factory, BASF is currently utilizing industrial textile waste from the textile production process and will gradually increase the share of post-consumer waste. These materials include cut edges, defective cut edges, leftovers, and other production textile waste from the textile industry. These materials are collected and provided to BASF by customers and partners. Discarded clothing made from polyamide 6 and other textile products can also be used for Loopamid production. All these waste materials are difficult to recycle because they typically consist of mixtures of different fibers, materials, dyes, and additives. Furthermore, for post-consumer waste recycling, buttons, zippers, and accessories must be removed in advance. BASF collaborates closely with partners and customers to accelerate the development of collection and sorting systems.
About Loopamid
BASF has developed an innovative solution through Loopamid to enhance the circularity of the fashion industry and recycle polyamide 6 textile waste. Thanks to its ability to tolerate all fabric mixtures including PA6 and elastane fibers, the technology behind Loopamid allows for textile-to-textile recycling of both post-industrial and post-consumer textile waste. Fibers and materials can be recycled multiple times, while maintaining material properties equivalent to those of traditional virgin polyamides.
【Copyright and Disclaimer】The above information is collected and organized by PlastMatch. The copyright belongs to the original author. This article is reprinted for the purpose of providing more information, and it does not imply that PlastMatch endorses the views expressed in the article or guarantees its accuracy. If there are any errors in the source attribution or if your legitimate rights have been infringed, please contact us, and we will promptly correct or remove the content. If other media, websites, or individuals use the aforementioned content, they must clearly indicate the original source and origin of the work and assume legal responsibility on their own.
Most Popular
-

Overseas Highlights: PPG Establishes New Aerospace Coatings Plant in the US, Yizumi Turkey Company Officially Opens! Pepsi Adjusts Plastic Packaging Goals
-
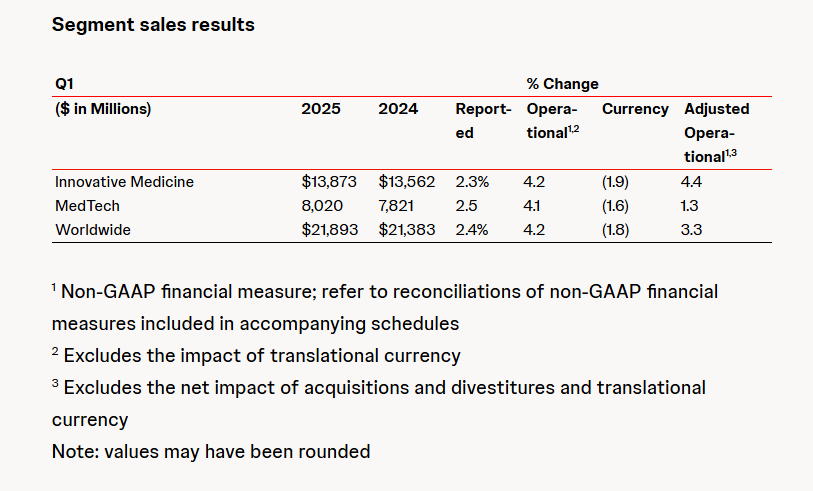
Abbott and Johnson & Johnson: Global Medical Device Giants' Robust Performance and Strategies Amid Tariff Pressures
-

BYD releases 2024 ESG report: Paid taxes of 51 billion yuan, higher than its net profit for the year.
-

Behind pop mart's surging performance: The Plastics Industry Embraces a Revolution of High-End and Green Transformation
-
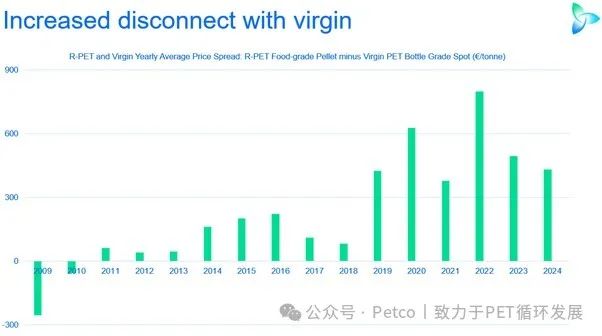
The price difference between recycled and virgin PET has led brands to be cautious in their procurement, even settling for the minimum requirements.



