Over 300 Employees Laid Off! Is Meina Unable to Cope?
On April 16, 2025, Illumina announced through an internal email a global workforce reduction of approximately 3.5% to advance its $100 million cost-cutting target. Based on the employee count of 8,970 at the end of 2024, this layoff affects over 300 people.

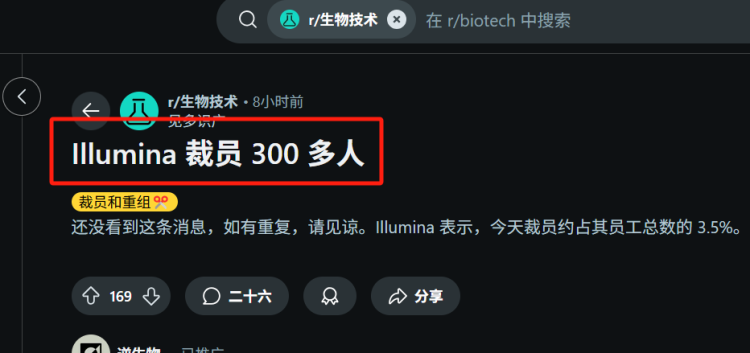
Illumina's layoffs are not an isolated incident, but part of a series of adjustments made in recent years. Since 2022, the company has implemented several layoff plans.
In 2022, Inmune announced a large-scale layoff, reducing approximately 500 employees globally, accounting for 5% of its total workforce. This layoff is seen as an important measure for Inmune to cope with cost pressures and changes in the industry.
2023 Multiple rounds of layoffs: Due to continued optimization of personnel structure at Meina, the specific number of layoffs has not been disclosed, but it involves multiple departments and regions.
In 2024, California Layoffs: Illumina terminated the positions of approximately 50 employees in California, signaling further adjustments in its U.S. domestic market.
In February 2025, 96 employees were laid off, mainly at the headquarters in San Diego, indicating that Illumina is still continuously optimizing its internal resource allocation.
This round of layoffs is Illumina's second layoff action after the major layoffs in February this year, but details such as specific layoff regions have not been disclosed yet. It remains unclear whether the layoffs are related to the business reduction caused by being included in the unreliable entity list by China's Ministry of Commerce.
On April 15, Jacob Thaysen, CEO of Illumina, stated during an interview at the 2025 Abu Dhabi Global Health Week that China remains a very significant market force, and they are exploring ways to bring gene sequencers back to China.
Jacob Thaysen emphasized in the above interview, "Our products are currently on the unreliable list, which means we cannot sell instruments to China. However, we will continue to provide consumables support to all our Chinese customers, especially Chinese patients who need high-quality sequencing to receive the right treatment."
Due to its long-term monopoly in the global gene sequencing market, Illumina is also known as the "Google" of the genetic technology industry. Public information shows that Illumina was founded in 1998 and is headquartered in the United States. As a leading company in the global gene sequencing field, its business covers oncology, genetics and infectious diseases, reproductive health, and other areas, with core products including high-throughput gene sequencers and gene chips.
Since entering the Chinese market in 2005, Illumina has held a significant position in China's gene sequencing instrument market. According to financial report data, in 2024, Illumina's revenue in China reached 2.2 billion yuan, with instrument revenue accounting for 20%-30% of the total.
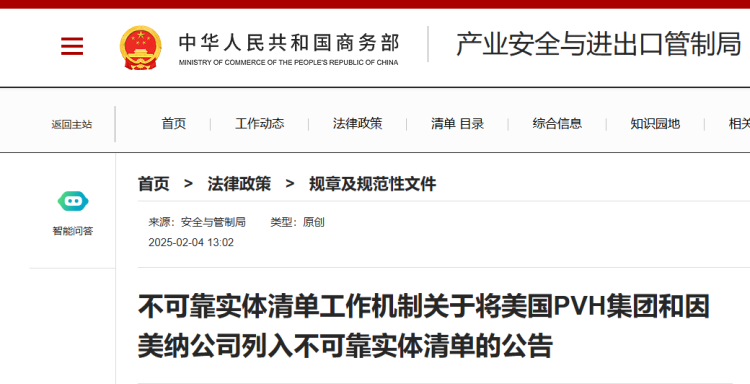
On February 4, China's Ministry of Commerce announced in a statement that Illumina was included in the "Unreliable Entities List" due to its violation of normal market transaction principles, interruption of normal transactions with Chinese enterprises, and discriminatory measures against Chinese enterprises, which severely harmed the legitimate rights and interests of Chinese enterprises.
It was also revealed by industry insiders that Meina suddenly interrupted cooperation with several Chinese biopharmaceutical companies under the pretext of "supply chain security review," even seizing already paid orders, which caused dozens of domestic cancer early screening and genetic disease research projects to be forced to halt.
The day after being included in the list, Illumina issued a statement saying that the company was "conducting a detailed assessment of the impact of the relevant matters and actively seeking solutions," while emphasizing that it "always adheres to market-oriented and rule-of-law principles in its global operations."
On March 4, the Chinese Ministry of Commerce announced the inclusion of the American company Illumina on the unreliable entity list and prohibited it from exporting gene sequencing instruments to China. This decision takes effect immediately upon announcement.
On March 11, Illumina responded to the aforementioned announcement, stating that it fully respects the decision of China's Ministry of Commerce and will continue to operate globally in accordance with market-oriented and legal principles, strictly complying with the laws and regulations of all countries or regions where it operates, including China.
In addition, Ankur Dhingra, the Chief Financial Officer of Mena, stated, "Our new guidance for fiscal year 2025 indicates that revenue contributions from China will be relatively limited, and we expect the current macro trends to persist."
In addition, Inmune has revealed that the company is developing an incremental cost reduction plan of about $100 million for the fiscal year 2025. These savings will help mitigate the impact of various potential scenarios related to the decline in revenue and associated operating income from its Greater China business.
On April 8, the 91st China International Medical Equipment Fair (CMEF) grandly opened at the National Exhibition and Convention Center (Shanghai), but Illumina did not attend the exhibition. It is widely believed that Illumina's absence may be related to its inclusion on the "Unreliable Entity List."
On the other hand, the industry generally believes that the ban on Illumina's export of gene sequencers to China is expected to accelerate the domestication process of China's gene sequencer market. A pharmaceutical researcher told the media in an interview that leading domestic companies such as MGI Tech and Genemind Biotech will benefit from this.
For BGI Genomics, the ban on high-end products imported from the United States makes it easier for domestic equipment to enter the market, boosting performance recovery, while also buying time for the research and development of a new generation of high-throughput sequencing devices.
According to media reports, in fact, some customers of Illumina have begun to switch to choose domestic options. Peking Union Medical College Hospital announced in April 2025 that it would suspend its collaboration with Illumina on a rare disease genomic program and instead adopt the BGI Genomics DNBSEQ-T20 sequencing platform.
The contraction of Illumina's business in the Chinese market had already become evident in previous years. According to financial reports, Illumina's market share in China's gene sequencing instrument and consumables market, calculated by annual revenue, has declined from 64.50% in 2021 to 54.2% in 2023.
Additionally, according to data from CIC, in 2023, MGI's market share in China has reached 47.3%, breaking Illumina's domestic monopoly.
【Copyright and Disclaimer】The above information is collected and organized by PlastMatch. The copyright belongs to the original author. This article is reprinted for the purpose of providing more information, and it does not imply that PlastMatch endorses the views expressed in the article or guarantees its accuracy. If there are any errors in the source attribution or if your legitimate rights have been infringed, please contact us, and we will promptly correct or remove the content. If other media, websites, or individuals use the aforementioned content, they must clearly indicate the original source and origin of the work and assume legal responsibility on their own.
Most Popular
-

Key Players: The 10 Most Critical Publicly Listed Companies in Solid-State Battery Raw Materials
-

Vioneo Abandons €1.5 Billion Antwerp Project, First Commercial Green Polyolefin Plant Relocates to China
-

EU Changes ELV Regulation Again: Recycled Plastic Content Dispute and Exclusion of Bio-Based Plastics
-

Clariant's CATOFIN™ Catalyst and CLARITY™ Platform Drive Dual-Engine Performance
-

List Released! Mexico Announces 50% Tariff On 1,371 China Product Categories






