Current Development Status of China's Agricultural Film Industry: Slight Recovery in Production, Significant Opportunities for the Development of Biodegradable Agricultural Films
Definition of agricultural film and industrial chain diagram
Agricultural film refers to the general term for plastic films used in agricultural production. It is the fourth largest agricultural production material after seeds, fertilizers, and pesticides, and plays a significant role in increasing temperature, retaining moisture, drought resistance, water conservation, and boosting yield and income. Since the 1960s, China began producing and using agricultural film. After more than 60 years of development, its industrial chain has continuously improved, providing strong support for the development of the agricultural film industry.
Specifically, the upstream of agricultural films involves raw material sectors, mainly including polyethylene, polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride, and polystyrene, etc.; the midstream involves the production and supply of agricultural films, which can be divided into light thin films, multi-purpose films, long-life films, biodegradable films, and insect-proof films according to different functions and uses; the downstream sector involves its end application scenarios, including farmland coverage, canal and water storage pool lining, edible fungus cultivation, and storage of green fodder, etc.
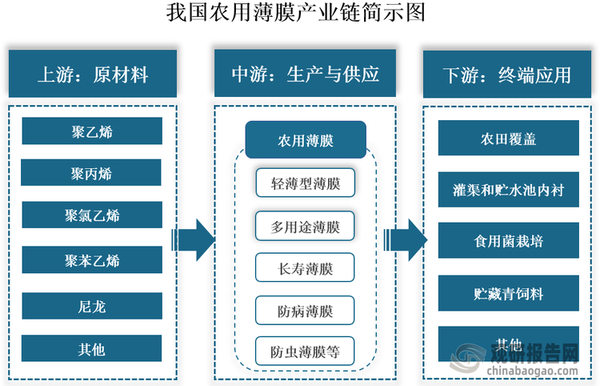
Source: Organized by Guanyan Tianxia
In the context of worsening white pollution, industry-related policies are becoming stricter.
Agricultural film is difficult to recycle and does not degrade easily, leading to "white pollution." This not only damages the landscape and destroys soil structure in farmlands, reduces soil permeability, hinders crop root growth, affects water and nutrient absorption, and results in reduced crop yields, but also causes pollution to soil, groundwater, surface water, plant crops, and the atmosphere due to residual film in the soil. If mistakenly consumed by animals, it can lead to animal deaths and even have an impact on human health.
With the increasing use of agricultural film, the "white pollution" caused by discarded agricultural film has increasingly become an important component of agricultural non-point source pollution. According to the second national pollution source census bulletin, the cumulative residual amount of plastic film in the country reached 1.1848 million tons by 2017. In order to prevent and control "white pollution" in farmland, China has successively issued multiple policies in recent years, including the "Action Plan for the Battle Against Agricultural and Rural Pollution," "Opinions of the National Development and Reform Commission and the Ministry of Ecology and Environment on Further Strengthening Plastic Pollution Control," and "Management Measures for Agricultural Film," which involve promoting the recycling and utilization of agricultural film, prohibiting the production and use of plastic film with a thickness of less than 0.01 millimeters, and strengthening the whole-process supervision of agricultural film, among other measures.
Policies Related to China's Agricultural Film Industry
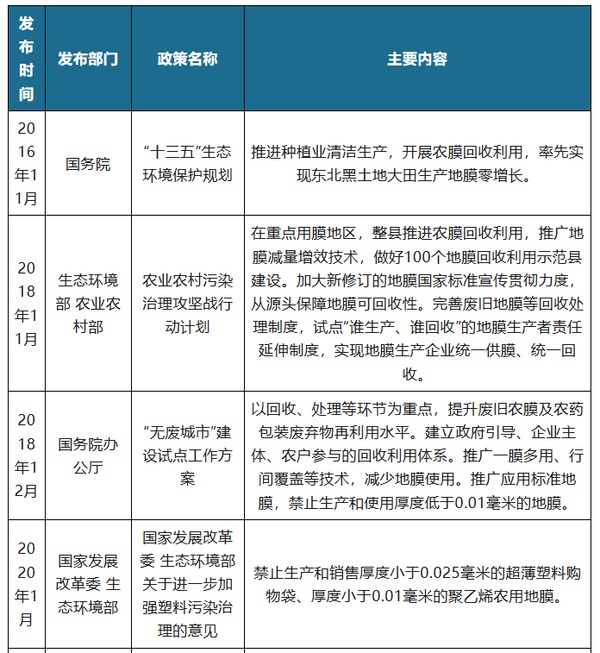
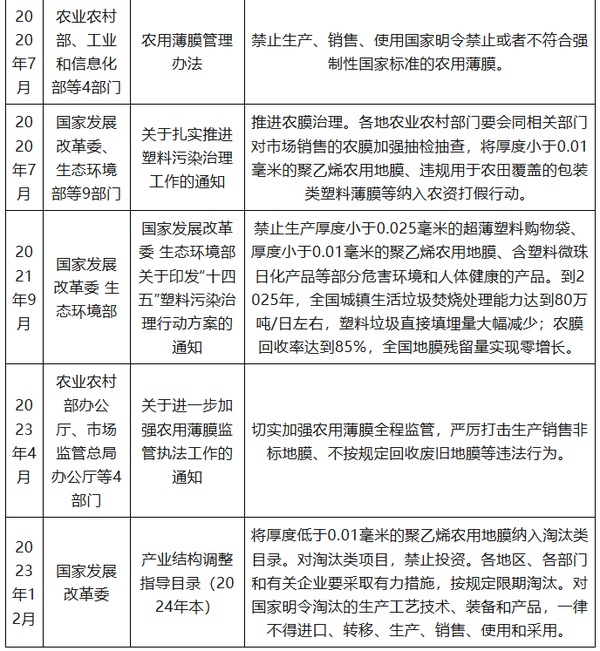
Source: Organized by Guanyan Tianxia
The production of agricultural film has rebounded, and its proportion of domestic plastic film production has been declining year by year.
Affected by the aforementioned policies, the production of agricultural films in China has shown a downward trend since 2017, dropping to 773,900 tons in 2020, a year-on-year decrease of 9.18%. Although the production of agricultural films continued to decline in 2019 and 2020, the rate of decline significantly slowed down against the backdrop of increasing application proportions of high-end agricultural films such as biodegradable films. By 2021, production had begun to slightly rebound to 798,700 tons, a year-on-year increase of 3.23%. In 2022, production continued to rise slightly, reaching approximately 831,700 tons, with a year-on-year growth of 4.11%.
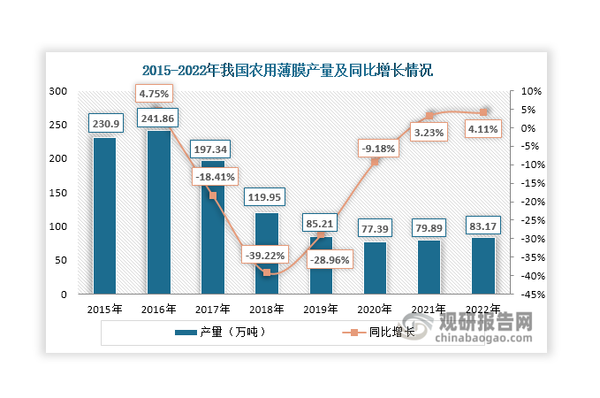
Data source: China Plastics Processing Industry Association, Guanyan Tianxia compilation
Agricultural film is one of the segmented markets of plastic film. In recent years, its proportion of the total plastic film production has shown a year-on-year decline, but the rate of decrease has gradually stabilized since 2021, reaching 4.91% in 2022.
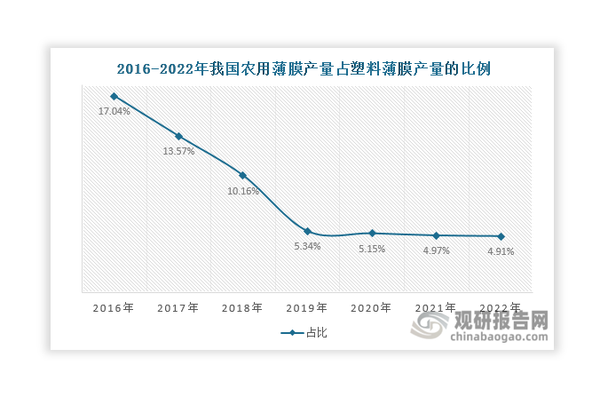
Data source: Guanyan Tianxia collation
The development opportunities for biodegradable agricultural films are significant, bringing new growth potential to the industry.
According to the report published by the Research and Consulting Network, "Deep Analysis of the Current Situation and Future Forecast of China's Agricultural Film Industry Report (2024-2031)》Shows that biodegradable agricultural films not only possess the functions and characteristics of traditional agricultural films such as polyethylene and polypropylene, but also have the advantages of being biodegradable and pollution-free. With the continuous advancement of the governance of "white pollution" in farmland, biodegradable agricultural film, as a substitute for traditional agricultural film, has a large substitution space. At the same time, national policies are also vigorously promoting the development of biodegradable agricultural film. The "Opinions of the CPC Central Committee and the State Council on Comprehensively Promoting Rural Revitalization and Accelerating the Modernization of Agriculture and Rural Areas", the "14th Five-Year Plan for National Agricultural Green Development Plan", the "14th Five-Year Plan for Promoting the Modernization of Agriculture and Rural Areas" and other policies have been successively introduced to accelerate the research and development and promotion of biodegradable agricultural film. Under the governance of "white pollution" in farmland and the promotion of policies, biodegradable agricultural film has ushered in major development opportunities, and also brought new growth space for the agricultural film industry.
Policies related to the degradable film industry in China
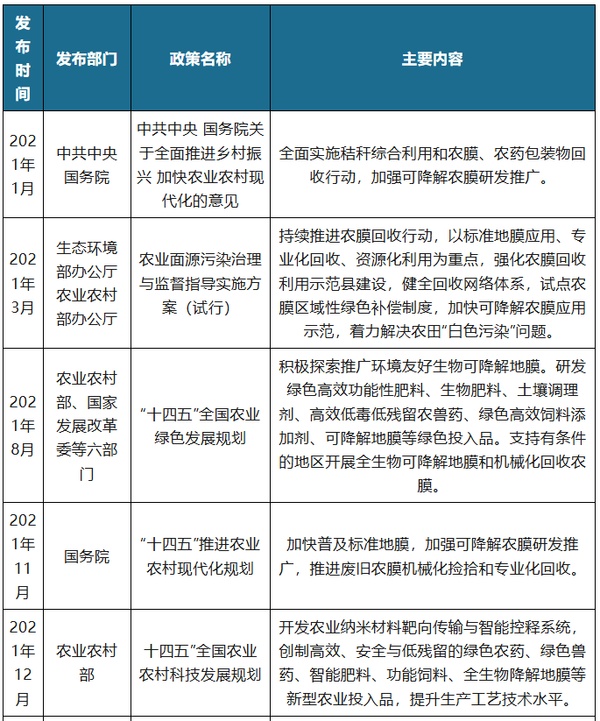
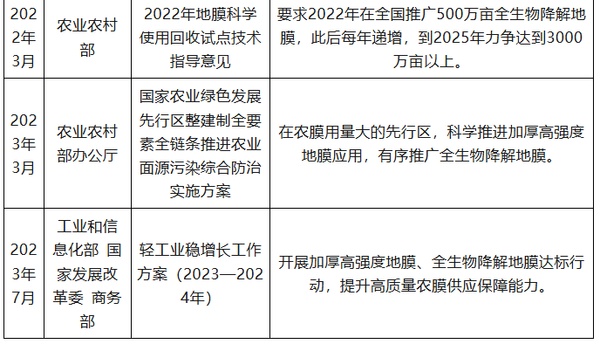
Source: Organized by Guanyan World
It is worth mentioning that due to factors such as the underdevelopment of biodegradable film technology, the low number of manufacturers, and high raw material prices, the cost of biodegradable agricultural films is relatively high compared to traditional agricultural films. It is reported that the input cost of biodegradable film per acre is about three times that of polyethylene film, which also reduces farmers' willingness to adopt it. However, several regions, including Fujian Province, Guizhou Province, and Hunan Province, have introduced subsidy policies for biodegradable agricultural films, which will help narrow the price gap between biodegradable and traditional films, benefiting its application and penetration. In the future, with the promotion of favorable industry policies, gradual maturity of technology, an increase in manufacturers, a decrease in raw material prices, and the expansion of local subsidy policies, it is expected that the market penetration rate of biodegradable agricultural films will continue to rise.
2023-2024 Subsidy Situation for Biodegradable Agricultural Films in Certain Areas
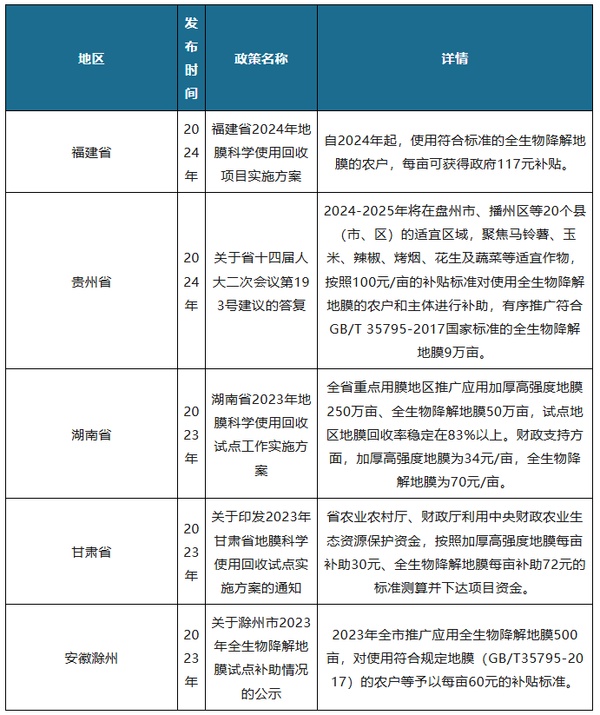
Source: Public information, organized by Guanyan Tianxia (WJ)
【Copyright and Disclaimer】The above information is collected and organized by PlastMatch. The copyright belongs to the original author. This article is reprinted for the purpose of providing more information, and it does not imply that PlastMatch endorses the views expressed in the article or guarantees its accuracy. If there are any errors in the source attribution or if your legitimate rights have been infringed, please contact us, and we will promptly correct or remove the content. If other media, websites, or individuals use the aforementioned content, they must clearly indicate the original source and origin of the work and assume legal responsibility on their own.
Most Popular
-

Key Players: The 10 Most Critical Publicly Listed Companies in Solid-State Battery Raw Materials
-

Vioneo Abandons €1.5 Billion Antwerp Project, First Commercial Green Polyolefin Plant Relocates to China
-

EU Changes ELV Regulation Again: Recycled Plastic Content Dispute and Exclusion of Bio-Based Plastics
-

Clariant's CATOFIN™ Catalyst and CLARITY™ Platform Drive Dual-Engine Performance
-

List Released! Mexico Announces 50% Tariff On 1,371 China Product Categories






