Nexam Chemical will develop next-generation composites for light aircraft.
Nexam Chemical, in collaboration with partners, is advancing the future of high-performance composites through the TAPE-X (Thermoforming Advanced Polymer Unidirectional Tape - TAPE-Extreme) project funded by Innovate UK.
The project is dedicated to developing next-generation composite materials capable of replacing metals like titanium in aerospace applications, making aircraft lighter and more fuel-efficient.
UD tape has storage stability and ease of processing.
The core of the project is the newly developed unidirectional (UD) tape. It aims to combine the storage stability and processability of thermoplastic tapes with the thermomechanical properties of thermosetting materials. Nexam Chemical contributes its unique experience in high-temperature material formulations in the design and synthesis of the matrix materials that serve as the conceptual basis. This innovation paves the way for the cost-effective production of complex geometries, such as pipes and ducts in aircraft engines, with greater precision and minimal waste.
"TAPE-X is an important step forward in composite material development. By combining ease of processing with excellent thermal and mechanical properties, we are unlocking new possibilities for industries such as aerospace, defense, and others that require extreme performance," said Christer Svanberg, Chief Technology Officer of Nexam Chemical.
The major advancements of TAPE-X technology
Enhanced processing window and storage stability: Unlike traditional thermoset materials, the new resin has a wide processing window and excellent stability, eliminating the need for low-temperature storage.
Heat resistance: This material is specifically designed to meet the high thermal demands of aerospace applications, capable of withstanding extreme conditions, serving as a lightweight alternative to titanium and other alloys.
Enhanced design flexibility: The combination of thermoplastic-like processing and thermoset-level performance enables the creation of complex structures that would otherwise be difficult to manufacture or costly.
Vast Industrial Potential: Although the technology was initially focused on civilian aerospace applications, it is expected to be applicable to other aerospace and industrial uses where extremely high heat resistance and structural integrity are crucial.
【Copyright and Disclaimer】The above information is collected and organized by PlastMatch. The copyright belongs to the original author. This article is reprinted for the purpose of providing more information, and it does not imply that PlastMatch endorses the views expressed in the article or guarantees its accuracy. If there are any errors in the source attribution or if your legitimate rights have been infringed, please contact us, and we will promptly correct or remove the content. If other media, websites, or individuals use the aforementioned content, they must clearly indicate the original source and origin of the work and assume legal responsibility on their own.
Most Popular
-

Overseas Highlights: PPG Establishes New Aerospace Coatings Plant in the US, Yizumi Turkey Company Officially Opens! Pepsi Adjusts Plastic Packaging Goals
-
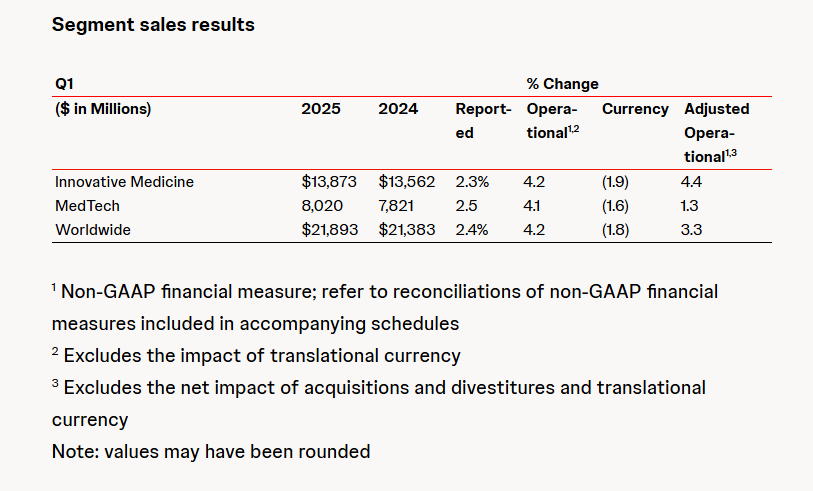
Abbott and Johnson & Johnson: Global Medical Device Giants' Robust Performance and Strategies Amid Tariff Pressures
-

BYD releases 2024 ESG report: Paid taxes of 51 billion yuan, higher than its net profit for the year.
-

Behind pop mart's surging performance: The Plastics Industry Embraces a Revolution of High-End and Green Transformation
-
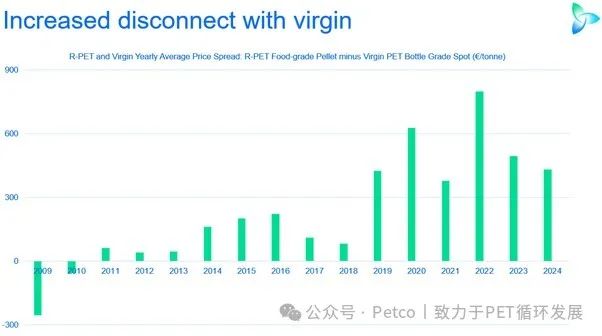
The price difference between recycled and virgin PET has led brands to be cautious in their procurement, even settling for the minimum requirements.



