Prohibited Substances | California, USA, Proposes Ban on Intentional Addition of Bisphenols, Antimony Trioxide, and Phthalates in Food Packaging
On February 20, 2025, California introduced Assembly Bill 1148, the "Safer Food Packaging Act of 2025." It aims to further strengthen the regulation of harmful substances in food packaging to protect public health and environmental safety.
On March 28, 2025, California made its first amendment to this bill.
Bill control details
Starting January 1, 2027, California will ban the intentional addition of the following three categories of substances in food packaging* (with content below the limit values specified in subsequent regulations):
Biphenolic substances (referring to two phenolic rings connected by a linking atom. The linking atom and the phenolic rings may also have additional substituents, excluding tetramethyl bisphenol F (TMBPF, CAS 5384-21-4));
Antimony trioxide
Phthalate esters
Food packaging refers to nondurable packaging, packaging components, or food service ware used for containing, serving, storing, handling, protecting, or selling food, food ingredients, or beverages, including but not limited to food or beverage containers, takeaway food containers, product boxes, liners, wrapping paper, utensils, straws, food boxes, and single-use plates, bowls, or trays.
Related substance background
Bisphenol compounds
Industry Applications: Bisphenol compounds are widely used in food contact materials due to their excellent chemical stability and heat resistance, such as polycarbonate (PC) plastic bottles, epoxy resin coatings (can lining), and thermal sensitive receipt paper.
Health risks: Bisphenols are typical endocrine disruptors, and long-term exposure may lead to immune system damage, reproductive health issues, and even cancer.
Antimony trioxide
Industry application: Used for flame retardant modification of plastics such as polypropylene (PP) and polyethylene (PE), commonly found in microwave meal containers and ready-to-eat food containers.
Health risks: Long-term exposure to antimony trioxide may cause irritation to the respiratory system and skin, and carries certain carcinogenic risks.
Phthalates
Industrial application: As the main plasticizer for PVC plastics, commonly found in food packaging films, bottle cap sealing rings, and soft tubes.
Health Risks: Phthalates have reproductive toxicity, liver damage risks, interfere with the normal function of the endocrine system, affect metabolism, and increase the risk of diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
In recent years, there has been increasing global attention to the safety of food contact materials. For these three types of substances, various countries and regions have successively introduced relevant control measures, such as:
In May 2022, the U.S. FDA amended the food additive regulations (21CFR-Title21) by removing 25 previously authorized phthalates used as (indirect) food additives.
In October 2023, the U.S. Congress introduced the H.R. 6105 bill, known as the **Toxic-Free Food Packaging Act of 2023 (proposed bill)**, which identified five categories of substances as unsafe for use in food contact materials. These include bisphenol A, B, S, F, AF or related compounds, antimony trioxide, and phthalates.
In December 2024, the European Union officially passed regulations banning the use of Bisphenol A in food contact materials. These measures indicate that banning harmful substances in food contact materials has become a global trend.
【Copyright and Disclaimer】The above information is collected and organized by PlastMatch. The copyright belongs to the original author. This article is reprinted for the purpose of providing more information, and it does not imply that PlastMatch endorses the views expressed in the article or guarantees its accuracy. If there are any errors in the source attribution or if your legitimate rights have been infringed, please contact us, and we will promptly correct or remove the content. If other media, websites, or individuals use the aforementioned content, they must clearly indicate the original source and origin of the work and assume legal responsibility on their own.
Most Popular
-

Overseas Highlights: PPG Establishes New Aerospace Coatings Plant in the US, Yizumi Turkey Company Officially Opens! Pepsi Adjusts Plastic Packaging Goals
-
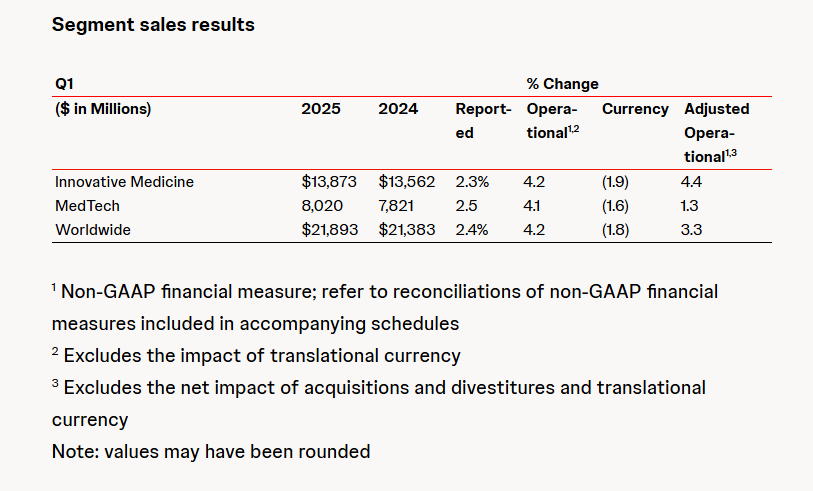
Abbott and Johnson & Johnson: Global Medical Device Giants' Robust Performance and Strategies Amid Tariff Pressures
-

BYD releases 2024 ESG report: Paid taxes of 51 billion yuan, higher than its net profit for the year.
-

Behind pop mart's surging performance: The Plastics Industry Embraces a Revolution of High-End and Green Transformation
-
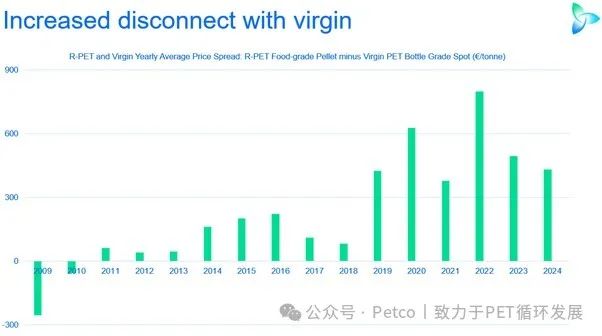
The price difference between recycled and virgin PET has led brands to be cautious in their procurement, even settling for the minimum requirements.



