Leading Modified Plastics Company Opens Doors to Humanoid Robot Industry with Innovative Materials
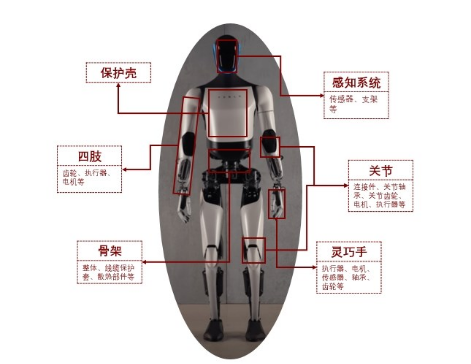
When Tesla's Optimus Gen-2 shocked the industry with a 10 kg weight reduction and a 30% speed increase, few noticed the key behind this breakthrough—material innovation. As a comprehensive product that integrates mechanics, electronics, and AI, humanoid robots' mobility, endurance, and lifespan have always been limited by material performance. Joint components must withstand fatigue tests of millions of flexions and extensions, the skeletal structure must find a balance between lightweight design and load-bearing capability, and electronic components rely on high-temperature and high-insulation packaging for protection.
As a global leader in the modified plastics field, Kingfa Sci. & Tech. Co., Ltd. is one of the most comprehensive enterprises in the global chemical new materials industry in terms of product variety. It is also the largest modified plastics manufacturer in the world with the most comprehensive range of products.

In the fields of biodegradable plastics, specialty engineering plastics, carbon fiber, and composite materials, the company's product technology and product quality have reached an internationally advanced level. The company has established a complete industrial chain around polymer materials, gradually highlighting the advantages of industrial synergy, and has achieved an upgrade from single modified plastics to a variety of new chemical materials. The product structure is continuously extending towards the high-end and high value-added direction of the industry.
1
Technological Breakthrough:
Special materials solve the core pain points of humanoid robots.
The "walking and thinking" of humanoid robots is always constrained by material performance. Joints need to be wear-resistant and temperature-resistant, the skeleton must be lightweight and high-strength, and circuits require shielding and protection. These multiple demands have led to an urgent need for advanced materials. Jinfa Technology's solution lies in breakthroughs in three core types of materials.
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK)PEEK):As a "noble" among engineering plastics, the large-scale application of PEEK materials is a milestone. As early as 2013, Jinfeng Technology initiated this ten-year research and development project, and now its independently developed high-temperature-resistant PEEK composite materials have achieved mass supply. This material not only significantly reduces the weight of Tesla's Optimus but also addresses the wear and tear issues faced by leading manufacturers like Yushu Technology in robotic joints during long-term use. In precision components such as dexterous hand skins and actuator gears, the self-lubricating properties of PEEK greatly extend the lifespan of robots.
Application Areas of PEEK Materials Source: Tesla, Minsheng Securities Research Institute
Polyamide(PA):The polyamide series materials can construct the "skeleton" of robots. The LFT-PA (Long Fiber Reinforced Polyamide with good appearance and high strength) developed by Jinfat Technology has a density that is more than 30% lower than that of traditional steel, while its tensile strength can reach 250 MPa, and its bending modulus can reach 15,000 MPa. This solution of "using plastic instead of steel" with LFT-PA materials can be applied to structural components such as the chest support and connecting rods of robots.
Liquid Crystal Polymer(LCP):LCP materials have characteristics such as high-temperature resistance and low dielectric loss, making them suitable for precision electronic components like servo motors and connectors. They can meet the high-frequency signal transmission requirements of AI servers and robots. With good fluidity and dimensional stability, LCP materials are one of the best material choices for precision components, including micro motors and high-frequency signal connectors. The servo motors corresponding to the over 40 joints of humanoid robots all require connectors with stable high-frequency dielectric properties. Kingfa Technology's LCP materials have a dielectric constant as low as 3.0 and a dielectric loss of less than 0.002, with signal attenuation in the frequency range above 15 GHz significantly lower than that of traditional MPI materials, ensuring real-time response of motor commands.
2
Ecological layout:
"Capital + Industry" binding top players
Beyond technological breakthroughs, Kingfa Technology has deeply embedded itself into the global robotics supply chain through a dual-wheel model of "industry collaboration + capital linkage." Through the Jinshi Growth Fund, the company indirectly holds a 0.32% stake in Unitree Robotics, a leading domestic robotics company. This "equity + business" binding model ensures a stable supply of PEEK joint materials to Unitree's production lines.
In the international market, Kingfa Science & Technology has successfully become part of Tesla's core supply chain system, with its collaboration extending from automotive materials to the advanced field of humanoid robots, achieving deep cross-scenario coordination. In the automotive sector, the focus is on the demand for Tesla's vehicle interior and exterior components, providing specialized materials that meet its production standards. In the humanoid robot domain, Kingfa closely follows the development and mass production pace of Tesla's humanoid robot, Optimus, supplying PEEK materials with characteristics such as high strength, wear resistance, and high and low-temperature resistance, ensuring material support for the mechanical performance and operational stability of Optimus.
Future Prospects
Despite the current small sales proportion of robotic materials, Kingfa Sci & Tech's strategic layout has already demonstrated long-term value. As the costs of materials like PEEK decrease and application scenarios expand, the company is poised to benefit not only from the mass production wave of humanoid robots but also potentially extend into fields such as low-altitude economy and intelligent driving. The transformation of this material giant is proving an industry logic: the competition in humanoid robots ultimately boils down to a competition of materials.
【Copyright and Disclaimer】The above information is collected and organized by PlastMatch. The copyright belongs to the original author. This article is reprinted for the purpose of providing more information, and it does not imply that PlastMatch endorses the views expressed in the article or guarantees its accuracy. If there are any errors in the source attribution or if your legitimate rights have been infringed, please contact us, and we will promptly correct or remove the content. If other media, websites, or individuals use the aforementioned content, they must clearly indicate the original source and origin of the work and assume legal responsibility on their own.
Most Popular
-

India's Q3 Smartphone Shipments Rise 3%; Japanese Mold Factory Closures Surge; Mercedes-Benz Cuts 4,000 Jobs
-

Ascend's Restructuring Plan Approved! Jwell Launches Global Acceleration Plan; Nexperia Chip Crisis Threatens Global Auto Production
-

Dow To Restart Pe Units 5 And 7 This Week, Recovery Date For Unit 6 Remains Undetermined In The United States (US)
-

Key Players: The 10 Most Critical Publicly Listed Companies in Solid-State Battery Raw Materials
-

The Roller-Coaster Behind Sanhua Intelligent Controls' Stock Price: What Are the Advantages of Automotive Thermal Management Companies Crossing Into Humanoid Robots?






