The Ultimate Guide to Silane Dispersants! Four Major Performance Advantages and Core Filler Processing Guidelines
Silane has a wide range of applications! They act as coupling agents and dispersants for fillers in rubber and plastic formulations, serve as polymerization modifiers in polypropylene synthesis, and can also be used as cross-linking agents for polyethylene homopolymers and copolymers. With their unique properties, silanes are used to enhance the processing performance and product performance in the plastics and rubber industries.
This guide will focus on the advantages of silane as a dispersant and key points for selection. You will better understand the mechanism of action of silane in plastics and rubber and learn how to choose the type of silane that is most suitable for your application.

Silane's chemical structure
Silane is a molecule with a central silicon atom connected to two types of groups: alkoxy groups and organic functional groups.
The general structure of silane is as follows:Y-R-Si-X₃
Among them:
X represents a hydrolyzable alkoxy group (methoxy, ethoxy, or acetoxy).
Y represents the organic functional groups (amino, vinyl, epoxy, methacryloxy, etc.) connected to silicon atoms via alkyl bridges R.
These two types of groups have different reactivity, allowing for sequential reactions.
Building on this, we will next explore how silane can improve the dispersibility in filled plastics and elastomers.
Silane as a dispersant
Dispersants are used to promote and stabilize the dispersion of solid ingredients such as fillers or pigments in a polymer (or liquid resin) matrix. Better dispersion leads to improved processing performance and superior material properties!
Silane is such an additive that helps improve processing efficiency or product performance and has cost advantages.
The following will outlineHow silanes improve the dispersibility of pigments and fillers in plastics, and how they help enhance the processing performance and properties of materials.
Dispersion mechanism of silane.
During the silane treatment of fillers or pigments, the functional groups (such as hydroxyl groups) of the fillers or pigments react with the alkoxy groups of the silane, forming a silane-functionalized surface.
The surface of the filler is functionalized through specific interactions or chemical reactions between the polymer and the silane organic functional groups, thereby enhancing compatibility with the polymer matrix. The selection of silane functional groups needs to match the polymer matrix.
Silane treatment can also form a "protective layer" to prevent particles from re-aggregating. The following figure illustrates the process of treating mineral surfaces with organosilanes:
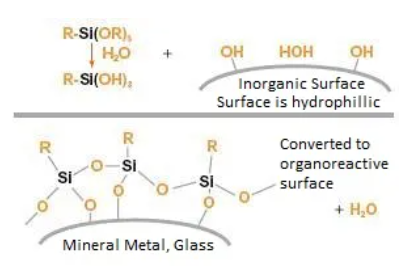
Silane surface treatment diagram
Advantages of silane dispersants
Using silane dispersants in the formulation of thermoplastic plastics, rubber, or thermosetting plastics can bring multiple advantages, ultimately resulting in easier processing and/or better product performance. When producing masterbatches, using silane-treated pigments can achieve higher pigment loading levels or faster production efficiency.
Using silane as a dispersant has significant performance and cost advantages.
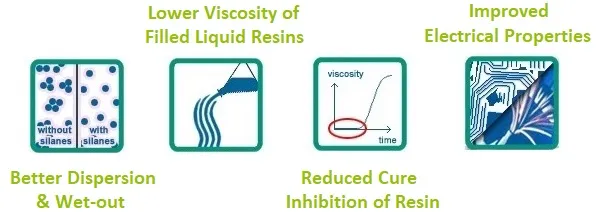
Understand the various advantages provided by silane dispersants for materials, or click on specific advantages to address corresponding issues.
Better dispersion and wettability
Reduce the viscosity of the filled liquid resin.
Reduce resin cure inhibition
Improve electrical performance
01
Better dispersion and wettability.
The use of silane dispersants can significantly improve the dispersion of fillers and pigments in polymer systems (applicable to thermosetting plastics, thermoplastic plastics, and even rubber elastomer networks).
This is attributed to the modification of the filler surface, which enhances its compatibility with the polymer matrix and improves the wettability of the filler. For example, XIAMETER™ Z-6070 silane can also form a "protective layer" that minimizes particle re-agglomeration and shields the surface from affecting resin curing and electrical performance.
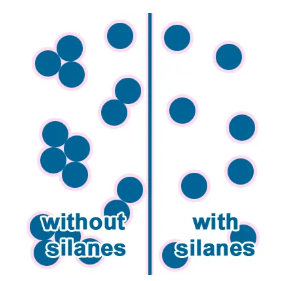
Comparison diagram of filler treated with silane and untreated filler.
For thermoplastic plastic systems, improving dispersibility can bring:
Easier to add fillers or pigments (higher filling rate, wider processing window)
Lower material viscosity
Reduce surface defects
Better mechanical properties
Pigments with better hiding power (such as titanium dioxide TiO₂)
For liquid resin systems, improving dispersibility typically means reducing residual bubbles and lowering slurry viscosity, thereby enhancing flowability during molding and allowing for a higher proportion of low-cost fillers to be used.
02
Reduce viscosity
Adding fillers to molten polymers often increases the melt viscosity of the mixture. The increase in viscosity depends on various parameters, such as:
Viscosity of molten polymer
Filler concentration
The quality of wetting between polymer and filler
Particle Size Distribution
Treating filler particles with silane can improve the wettability of the polymer towards the filler, helping to maintain good dispersion of the fillers, which results in a lower viscosity of the composite compared to using untreated fillers. This aids in enhancing processing performance, increasing yield, improving surface quality, and increasing the filler loading in the masterbatch.
Silane-treated fillers and pigments can achieve higher output, better surface quality, and higher fill levels.
The following figure shows the effect of silane treatment on melt temperature and torque percentage during the production process of PE/TiO₂ masterbatch filled with 80% TiO₂.
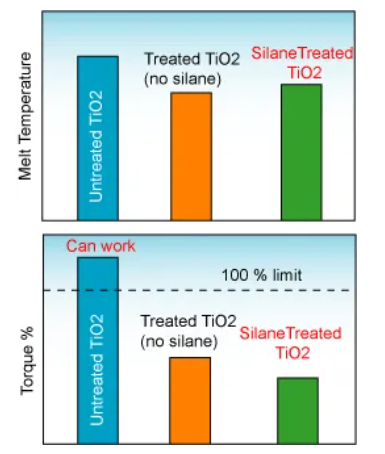
Silane-treated TiO₂ enables lower torque and higher yield.
03
Reduce solidification suppression
It is known that fillers can have varying degrees of inhibitory effects on the curing system of thermosetting resins. Using silane as a dispersant can reduce this curing inhibition.
Silanization of fillers in polyester and epoxy resins often overcomes the curing inhibition problem indicated by the exothermic curve of curing (see the figure below). Usually, the most effective silane dispersants tend to achieve the highest exothermic peak.
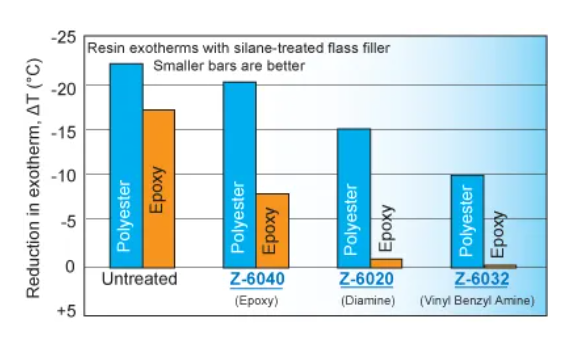
The silanes with the highest exothermic peaks are usually the most effective dispersants.
04
Improving electrical performance
The ability of silane dispersants to enhance electrical performance is demonstrated in the table below, using quartz-filled epoxy resin as an example.
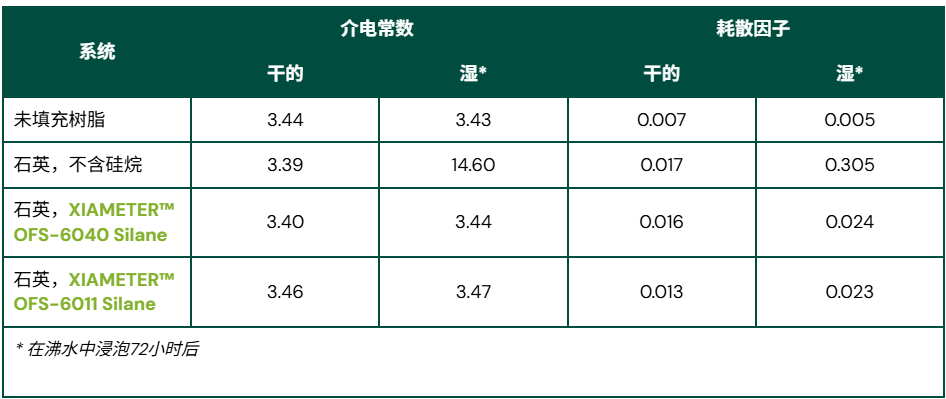
Unfilled epoxy resin exhibits good electrical properties, dielectric constant, and loss factor even after 72 hours of boiling water aging. However, after adding quartz filler, the hydrophilic surface of quartz leads to a severe decline in electrical properties during boiling water tests. After treatment with XIAMETER™ OFS-6040, OFS-6011, or OFS-6070 silane, the retention rate of electrical properties of quartz-filled composites is significantly improved.
Silane dispersant treatment of fillers
Mineral fillers have become increasingly important additives and modifiers for organic polymers. Silanes are naturally suited to treat mineral surfaces to enhance their dispersion in polymers.
The different applications of silane dispersants in mineral processing include:

Advantages of silane-treated fillers:

01
Titanium dioxide (TiO₂) treatment
TiO₂ is the most commonly used white pigment in plastics, known for its excellent whiteness, opacity, and UV resistance. Most compounders and masterbatch producers require the following characteristics to maintain high-quality standards and price competitiveness.
Key requirements for materials or masterbatches containing TiO₂:
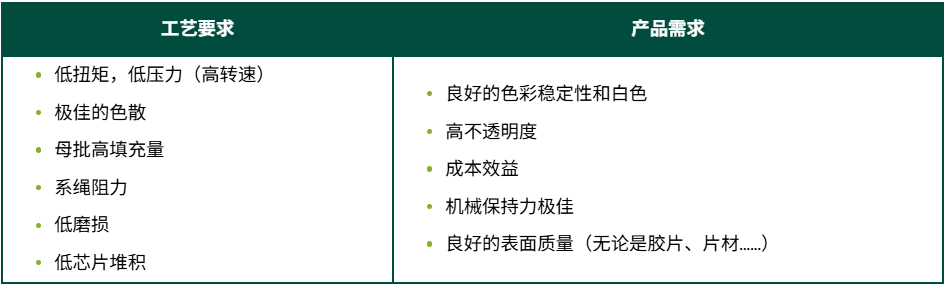
To achieve these requirements, TiO₂ is commonly treated with dispersants such as XIAMETER™ OFS-6070 silane.
Silane-treated TiO₂ can simultaneously enhance the dispersibility of TiO₂ and the performance of TiO₂-filled plastics.
The figure below shows how silane treatment reduces the melt temperature and the required torque in the production of PE/TiO₂ masterbatch filled with 80% TiO₂.
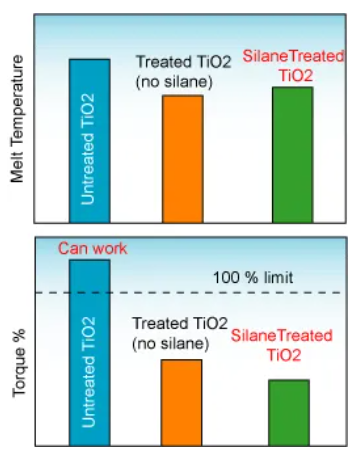
Silane treatment of fillers reduces melt temperature and torque in the mixer.
02
Talc powder treatment
Talc powder is a plate-like filler commonly used as a reinforcing agent for polyolefins (PE, PP, EVA), styrenic polymers, and some engineering plastics. It is used to improve heat deflection temperature (HDT) and stiffness, and can reduce creep, shrinkage rate, and coefficient of linear thermal expansion (CLTE).
To achieve these effects, talcum powder is often treated with dispersants such as XIAMETER™ OFS-6070 silane.
Talc powder treated with silane can enhance its dispersibility and the performance of talc-filled plastics.
03
Talc processing
Talc is a white fibrous filler that provides good dimensional stability, scratch resistance, and excellent stiffness to thermoplastic plastics such as PP or PA. It is mainly used in automotive parts such as decorative strips, bumpers, or dashboards.
Treated with dispersants such as XIAMETER™ OFS-6070 Silane, wollastonite can achieve these properties.
Silane-treated wollastonite can improve dispersibility and enhance the performance of wollastonite-filled plastics.
【Copyright and Disclaimer】The above information is collected and organized by PlastMatch. The copyright belongs to the original author. This article is reprinted for the purpose of providing more information, and it does not imply that PlastMatch endorses the views expressed in the article or guarantees its accuracy. If there are any errors in the source attribution or if your legitimate rights have been infringed, please contact us, and we will promptly correct or remove the content. If other media, websites, or individuals use the aforementioned content, they must clearly indicate the original source and origin of the work and assume legal responsibility on their own.
Most Popular
-

Key Players: The 10 Most Critical Publicly Listed Companies in Solid-State Battery Raw Materials
-

Vioneo Abandons €1.5 Billion Antwerp Project, First Commercial Green Polyolefin Plant Relocates to China
-

EU Changes ELV Regulation Again: Recycled Plastic Content Dispute and Exclusion of Bio-Based Plastics
-

Clariant's CATOFIN™ Catalyst and CLARITY™ Platform Drive Dual-Engine Performance
-

List Released! Mexico Announces 50% Tariff On 1,371 China Product Categories






