Venezuela situation escalates, why is the crude oil market tense?
近期,委内瑞拉局势再度引发全球能源市场关注。作为拉美重要产油国,其原油产量虽不及巅峰时期,但仍是全球重质原油的重要供应来源之一。更关键的是,委内瑞拉是聚烯烃产业链上游——石脑油与乙烯裂解原料的重要潜在变量。一旦其出口受阻,将通过成本传导机制影响塑料等化工品价格。
The current market's main concern is whether the United States will militarily intervene in Venezuela. On the surface, this seems to be at odds with Trump's diplomatic style of "ending wars." He advocates for a quick resolution in the Russia-Ukraine conflict and promotes ceasefires in the Middle East, so why is he issuing military threats toward Venezuela?
The answer lies in the differences in geopolitical logic. Venezuela is not a "war hotspot" in the traditional sense, but rather a "strategic hidden danger" in the backyard of the United States. The Maduro government has long been regarded by the U.S. as an illegal regime and maintains close relationships with Russia and Iran. Especially as the Venezuelan presidential election approaches in 2024, the ban on opposition leader Maria Corina Machado from running has sparked strong dissatisfaction from the U.S. The Trump team has recently indicated that they "do not rule out any options," which is actually a pressure tactic intended to force Maduro to accept electoral reforms, rather than a genuine intention to launch a war.
In fact, the likelihood of the U.S. taking military action against Venezuela is very low. On one hand, the U.S. military is deeply engaged in strategic deployments in the Middle East and the Indo-Pacific, leaving little room to open a new front. On the other hand, Latin American countries generally oppose military intervention, with regional powers like Brazil and Argentina explicitly calling for a peaceful resolution. More importantly, if a conflict were to break out, oil prices could soar above $100, which would undermine the U.S. efforts to control inflation—this contradicts the economic goals of the Trump administration.
However, even without war, the risk of sanctions has already significantly impacted crude oil supply. At the end of 2023, the U.S. briefly eased sanctions on Venezuelan oil, allowing Chevron limited exports to alleviate global supply pressure. However, as the political situation deteriorated, the U.S. announced in November 2024 that it would tighten permits again, leading to an expected decline in Venezuela's crude oil exports by 150,000 to 200,000 barrels per day in December. Although this shortfall could be compensated by other OPEC+ members, the structural tightening of heavy crude oil may raise refining costs, indirectly supporting naphtha and ethylene prices, which in turn provides cost support for polyethylene and polypropylene.
Venezuela's crude oil production (currently at 1.13 million barrels per day)
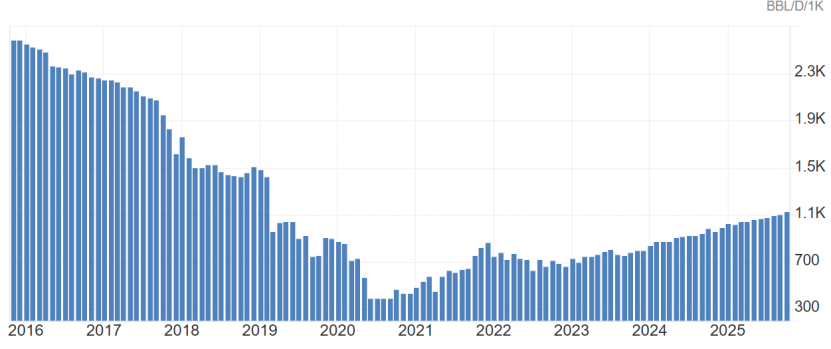
对聚烯烃市场而言,短期需警惕“地缘溢价”带来的成本扰动。若委内瑞拉出口持续受限,叠加北美冬季寒潮可能干扰乙烷供应,塑料期货或面临上行驱动。但中长期看,只要未发生实质性军事冲突,原油市场仍将回归供需基本面,委内瑞拉因素更多是情绪扰动而非趋势主导。
In summary, the United States and Venezuela are unlikely to engage in direct conflict, but they can certainly argue. This controllable geopolitical tension is becoming a new source of volatility in the crude oil and chemical markets.
Author: Zhou Yongle, Senior Market Analysis Expert

【Copyright and Disclaimer】This article is the property of PlastMatch. For business cooperation, media interviews, article reprints, or suggestions, please call the PlastMatch customer service hotline at +86-18030158354 or via email at service@zhuansushijie.com. The information and data provided by PlastMatch are for reference only and do not constitute direct advice for client decision-making. Any decisions made by clients based on such information and data, and all resulting direct or indirect losses and legal consequences, shall be borne by the clients themselves and are unrelated to PlastMatch. Unauthorized reprinting is strictly prohibited.
Most Popular
-

Dow, Wanhua, Huntsman Intensively Raise Prices! Who Controls the Global MDI Prices?
-

Clariant Unveils Cost-Cutting Plan Details, Plans to Shut Down Multiple Plants
-

[Today's Plastics Market] General Materials Weakly Fluctuate, Engineering Materials Steadily Rise
-

New Breakthrough in Domestic Adiponitrile! Observing the Rise of China's Nylon Industry Chain from Tianchen Qixiang's Production
-

Daily Review: Polyethylene Prices Under Weak Consolidation, Sellers Face Significant Pressure to Move Inventory






