Water-based release agent technology: Paving Innovative Paths for Weight Reduction in Aircraft

Technological Innovation: The Transition from Solvent-Based to Water-Based Solutions
Water-based release agents use water as the dispersing medium and employ nano-emulsion technology to evenly disperse active ingredients, forming a dense and stable separation film. Compared to traditional oil-based release agents, their core advantages are reflected in three aspects:
Environmental Friendliness: The water-based system reduces VOC emissions by over 90%, completely avoids flammability risks, and complies with EU REACH regulations and China's "dual carbon" strategy requirements. Measurements from an integrated die-casting production line of an automotive company show that after switching to a water-based release agent, the total non-methane hydrocarbons concentration in the workshop dropped from 120 mg/m³ to 15 mg/m³.
Surface quality control: The emulsion particle size is controlled to be below 0.6μm, ensuring coating uniformity. In the manufacturing of composite materials for aircraft skins, this technology reduces surface porosity by 70%, significantly decreasing subsequent repair processes and indirectly achieving structural weight reduction.
Process compatibility: The non-curing feature shortens mold preparation time by 80%. Combined with a micro-spray system, a single coating can support over a hundred release cycles, significantly improving production rhythm.
Weight loss mechanism: multidimensional efficiency enhancement
Water-based release technology achieves weight reduction goals through three main pathways:
Material utilization optimization: Precise demolding reduces edge waste, resulting in an increase in material utilization from 82% to 93% in the production of a certain type of helicopter rotor component, with a weight reduction of 4.7 kg per component.
Structural simplification: In conjunction with integrated die-casting technology, a water-based release agent addresses the demolding challenges of ultra-large components. A die-cast part for a certain new energy vehicle's rear floor has achieved the integration of 74 components, reducing weight by 30% while maintaining a demolding success rate of 99.2%.
Performance compensation design: Low transfer characteristics avoid the impact of release agent residue on the interlaminar bonding of composite materials, allowing designers to reduce redundant thickness by 3%-5%. In the manufacturing of satellite structural components, this technology optimized the thickness of carbon fiber laminates from 2.8mm to 2.3mm, achieving an overall weight reduction of 18%.

Industry Applications: Breakthroughs from Laboratory to Production Line
Precision component machining: Nanocellulose-enhanced coatings achieve sub-micrometer surface accuracy in the manufacture of satellite optical instrument supports, replacing traditional graphite coatings, reducing weight while improving thermal control performance.
Future Vision: The Integration of Intelligence and Sustainability
The evolution of technology presents three major trends:
Responsive material development: Thermosensitive release agents can automatically adjust their lubricity according to the mold temperature, maintaining stability within a wide temperature range of -40°C to 200°C, suitable for flexible production line needs.
Biobased raw material substitution: A third-generation water-based release agent based on starch derivatives has completed pilot testing, achieving a biodegradation rate of 92%. Commercialization is expected by 2028.
Digital Twin Integration: Real-time monitoring of release agent film thickness and status through IoT sensors, combined with AI algorithms to predict mold maintenance cycles, has achieved a 65% reduction in downtime on a pilot production line.

Water-based release agent technology not only redefines the environmental baseline of manufacturing processes but also opens up new weight reduction opportunities for aircraft design through the deep integration of materials science, surface engineering, and intelligent control. With breakthroughs in cutting-edge technologies such as nano-modification and bio-based materials, this green process will continue to drive aerospace manufacturing towards being lighter, stronger, and more sustainable.
【Copyright and Disclaimer】The above information is collected and organized by PlastMatch. The copyright belongs to the original author. This article is reprinted for the purpose of providing more information, and it does not imply that PlastMatch endorses the views expressed in the article or guarantees its accuracy. If there are any errors in the source attribution or if your legitimate rights have been infringed, please contact us, and we will promptly correct or remove the content. If other media, websites, or individuals use the aforementioned content, they must clearly indicate the original source and origin of the work and assume legal responsibility on their own.
Most Popular
-

Four Major Chemical New Material Giants Sell Off and Shut Down Again!
-
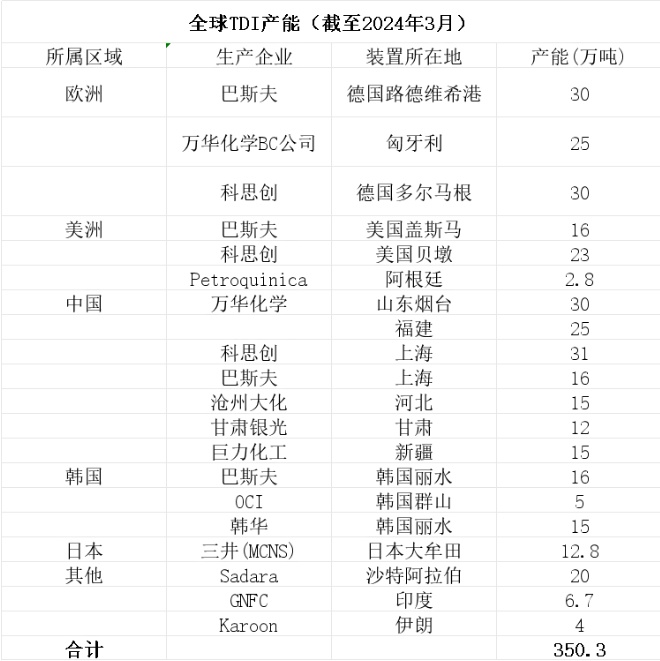
Covestro faces force majeure!
-

DuPont to Spin Off Nomex and Kevlar Brands for $14.4 Billion: Is Aramid Fiber Still Attractive?
-
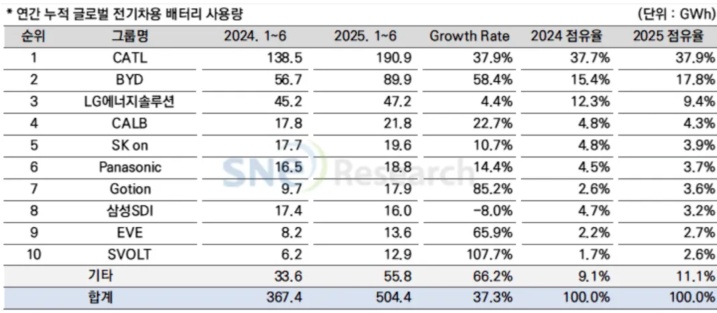
Massive Retreat of Japanese and Korean Battery Manufacturers
-

Napan Unveils Thermoplastic Composite Three-in-One Power System Solution, Battery Cover Weight Reduced by 67%



