Hidden PVC Stability Killer: Stabilizer Moisture Absorption and the Key Formulation Secrets
In the production of PVC products, formulation engineers often focus on primary stabilizers, lubrication systems, and processing techniques. However, a hidden yet crucial issue is frequently overlooked – composite calcium zinc. Hygroscopicity of various auxiliary additives in stabilizer formulationsThese materials, which quietly absorb moisture from the air, act like "Trojan horses" lurking within the system. They trigger a series of chain reactions during processing, ultimately leading to degraded product performance, aesthetic defects, and even large-scale scrapping.
I. The Core Hazards of Moisture Absorption: More Than Just "Dampness"
Water in high-temperature PVC processing (typically 160-200°C) can trigger multiple catastrophic consequences:
Direct degradationWater molecules at high temperatures promote the hydrolysis reaction of PVC resin, leading to the scission of molecular chains, directly reducing the degree of polymerization, and affecting mechanical properties.
Disrupting the established system.
Reacts with co-stabilizers such as calcium/zinc, consuming their active ingredients.
· Leading to phosphites and other auxiliary antioxidants Hydrolytic failure。
Premature deactivation of acid absorbers such as hydrotalcite.
Processing defects The rapid vaporization of water causes the melt to form.Bubbles, silver streaks, rough surface (orange peel) 。
Performance degradation Severely affects products / Significantly impacts products / Has a major impact on products Electrical insulation (decrease in volume resistivity), transparency (increase in haze), and long-term thermal aging performance 。
II. A "Moisture-Absorbing Culprit" Atlas in Formulations: From Obvious to Hidden
Common materials can be classified into the following categories based on their moisture absorption mechanisms and the severity of associated hazards:
Category 1: Highly Hygroscopic "Hazardous Materials" - Requires Strict Control
These materials possess high hydrophilicity due to their inherent chemical structure, or their physical structure readily traps water.
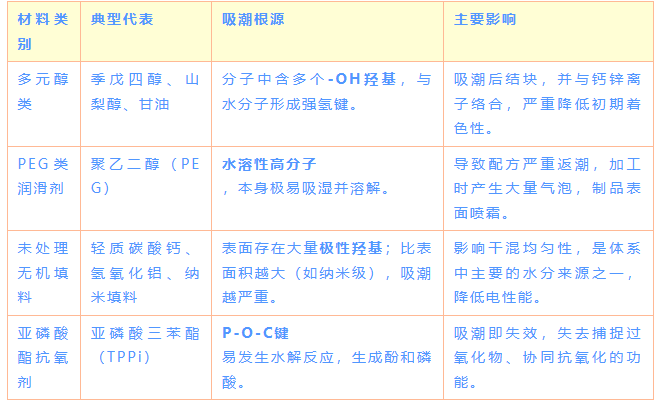
Category 2: Functional "Double-Edged Swords" — Small Dosage, Significant Impact
This material is a key functional component of the formulation, but its hygroscopic nature directly weakens its core function.
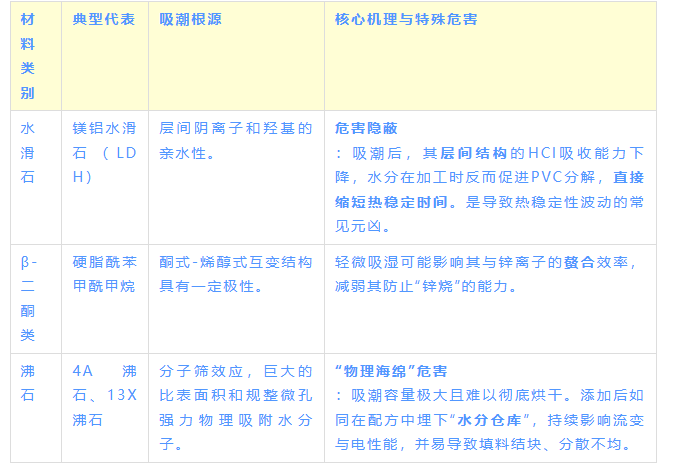
Category 3: The Hidden "Accomplice" - Purity is Key
While the material itself is not highly hygroscopic, it can act as a carrier for moisture if the quality is poor.
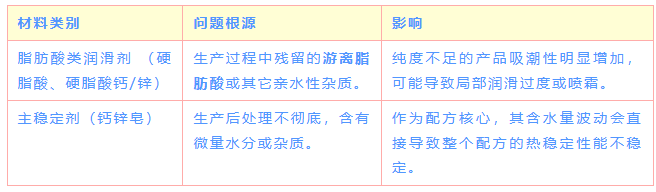
III. Systemic Solutions: End-to-End Control from Warehousing to Production
Step 1: Material Management and Pre-treatment (Fundamental Solution)
Strict WarehousingAll raw materials, especially the high-risk materials mentioned above, must be stored in sealed, cool, and dry conditions. Moisture-proof packaging with desiccant is recommended.
2. Required inspection before charging materials. Establish a moisture content monitoring program for hygroscopic materials (e.g., using a rapid moisture analyzer).
3. Drying:
High-risk materials (zeolites, inorganic fillers, polyols, etc.)
· Sensitive functional materials (hydrotalcites, β-diketones, etc.), but avoid overheating which leads to structural changes or decomposition.
Note: After drying, cool to room temperature and use immediately to prevent reabsorption of moisture.
Step 2: Recipe Optimization and Alternative Selection (Active Defense)
Preferred Hydrophobization ProductsSelect fillers (such as activated calcium carbonate, modified talc powder) that have been surface-modified with silane, stearic acid, etc.
2. Feature Replacement:
Replace some easily hydrolyzable phosphites with hindered amine light stabilizers (HALS) that have lower hygroscopicity.
Replace highly hygroscopic PEG lubricants with synthetic waxes, oxidized polyethylene waxes, and other alternatives.
3. Control the addition amount:Minimize the use of highly hygroscopic materials while meeting performance requirements.
4. Add moisture absorbents:Incorporating a small amount (0.2-0.5 phr) of hydrophobic fumed silica into the formulation can adsorb excess moisture and improve powder fluidity.
Step 3: Adjustment of Processing Technology (Emergency Remedy)
Strengthen dry mixing process. Ensure the high-speed mixer has a good heating and dehumidifying system. By increasing the mixing temperature (e.g., to 120℃) and extending the dehumidifying time, remove some loosely bound moisture.
2. Observe the melt state:During startup or material changes, closely observe the extruder vent for white smoke (water vapor) and the melt for bubbles. If abnormalities are present, immediately reduce screw speed, increase back pressure, and enhance venting.
IV. Summary and Core Recommendations
Hygroscopicity issues in a formulation is a... Systemic RiskTo solve it requires a comprehensive upgrade from "consciousness" to "action":
1. Develop "moisture-sensitive" awareness:Consider moisture content as a critical material attribute on par with "purity" and "particle size."
Grasp the principal contradiction. Focus onZeolites (physical water absorbers) Layered Double Hydroxide (Chemical Function Destroyer)These two types of materials, though vastly different in nature, both pose significant dangers.
Implement tiered management and control. Categorize materials by hygroscopic risk. Hierarchical ManagementDifferent storage, inspection, and pre-processing standards should be established.
4. Documentation and TraceabilityEstablish complete correlation records between material batches, pretreatment conditions, and final product performance, enabling rapid traceability to moisture issues when quality fluctuations occur.
Remember: On the battlefield of PVC stability, the invisible water molecules are often the enemy you need to be most wary of. Only through scientific identification and rigorous management can performance risks caused by moisture absorption be fundamentally eliminated, producing stable and reliable PVC products.
【Copyright and Disclaimer】The above information is collected and organized by PlastMatch. The copyright belongs to the original author. This article is reprinted for the purpose of providing more information, and it does not imply that PlastMatch endorses the views expressed in the article or guarantees its accuracy. If there are any errors in the source attribution or if your legitimate rights have been infringed, please contact us, and we will promptly correct or remove the content. If other media, websites, or individuals use the aforementioned content, they must clearly indicate the original source and origin of the work and assume legal responsibility on their own.
Most Popular
-

Key Players: The 10 Most Critical Publicly Listed Companies in Solid-State Battery Raw Materials
-

Vioneo Abandons €1.5 Billion Antwerp Project, First Commercial Green Polyolefin Plant Relocates to China
-

EU Changes ELV Regulation Again: Recycled Plastic Content Dispute and Exclusion of Bio-Based Plastics
-

Clariant's CATOFIN™ Catalyst and CLARITY™ Platform Drive Dual-Engine Performance
-

List Released! Mexico Announces 50% Tariff On 1,371 China Product Categories






