-
When BASF Lets "Agriculture" Fly Solo: Giant Slimming and Ambitions Under Capital Reassessment

BASF plans to spin off its Agricultural Solutions business unit on the Frankfurt Stock Exchange around 2025. This move reflects the strategic consideration of unlocking business value through capital operations and focusing on core businesses. In 202
ECHEMI -
Harvest Time! Disappearing Mulch Adds Buffs for a Bountiful Yield? How Incredible!

A seed, from falling to the ground to harvest. Behind it all are the hard work and dedication of agricultural workers. With the support of agricultural technology forces! "It is said that 'once the mulch is applied, yields increase quickly.'"
CHINAPLAS1 -
BDO Consumption Under Policy-Driven PBAT Mulch Film Promotion

In the process of managing agricultural film residual pollution in China, biodegradable mulch film with PBAT as the core raw material has become an important solution. Its promotion is closely related to comprehensive policy support. Against th
BDO Research Institute -
Three-Year Field Experiment Shows Biodegradable Mulch Increases Vegetable Yield by 46%

China Science Daily reports that the "white pollution" caused by traditional plastic mulch film has long been a pain point for agricultural environmental protection. Biodegradable mulch film is regarded as an alternative solution. However, does it ac
Bioplastics Research Institute -
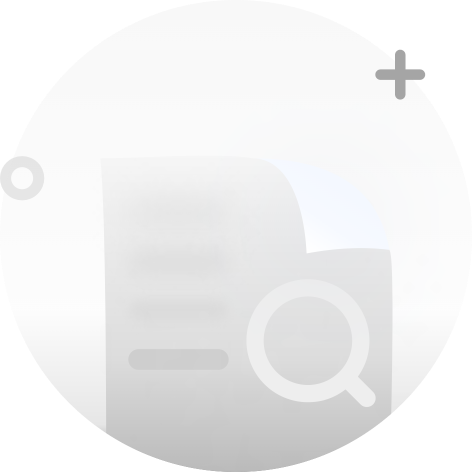
Guo baohua et al.: Production, Application, Issues, and Recommendations of Biodegradable Mulch Film
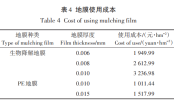
Title: Classification and Research and Development Application Status of Biodegradable Mulch Film Source: Journal of Agricultural Environmental Sciences, 2024, 43(6): 1278-1287. Authors: Zhang Mingming, Zhou Yingxin, Chen Jingwen, Xu Jun, Xu Ji
Bioplastics Research Institute -
Biodegradable film: Policy Support with Subsidies Ranging from 90 to 200 Yuan per Acre

Zhejiang Yuyao's total subsidy reaches 200 yuan per mu; Inner Mongolia Chifeng City's Ningcheng County subsidy reaches 170 yuan per mu; Shandong Guanquan County subsidy is 168 yuan per mu; Guizhou Province Yuqing County subsidy is 90 yuan per mu. Bio
Bioplastics Research Institute -
Policy Leads Green Transformation in Agriculture: Biodegradable Mulch Film Helps Shape New Rural Landscapes

In March 2025, the relevant policy announcements issued by the Ministry of Finance outlined a new direction for rural construction and agricultural development. Among the key initiatives, the third point—"advancing rural construction and governance i
Special Committee for Degradable Plastics -
Raw material inventory and prices both drop, demand for agricultural film weakens.
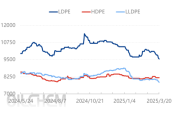
Recently, the inventory of polyethylene production enterprises in China has decreased by 6.68% compared to the previous period, and it has fallen by 24.04% from its peak this year. Enterprise proactive price reductions and inventory clearance, along
Longzhong -
Current Development Status of China's Agricultural Film Industry: Slight Recovery in Production, Significant Opportunities for the Development of Biodegradable Agricultural Films
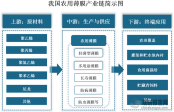
Definition of agricultural film and industrial chain diagramAgricultural film refers to the general term for plastic films used in agricultural production. It is the fourth largest agricultural production material after seeds, fertilizers, and pestic
Guanyan Tianxia -
New Advances in Agricultural Microplastics Research, Good News from Colombo!

From February 13 to 16, an academic exchange conference focusing on the Sino-UK agricultural microplastics project was held enthusiastically in Colombo, the capital of Sri Lanka. This meeting injected strong momentum into the deep advancement of the
Color Masterbatch Industry Network
Most Popular
-

Key Players: The 10 Most Critical Publicly Listed Companies in Solid-State Battery Raw Materials
-

Vioneo Abandons €1.5 Billion Antwerp Project, First Commercial Green Polyolefin Plant Relocates to China
-

EU Changes ELV Regulation Again: Recycled Plastic Content Dispute and Exclusion of Bio-Based Plastics
-

Clariant's CATOFIN™ Catalyst and CLARITY™ Platform Drive Dual-Engine Performance
-

List Released! Mexico Announces 50% Tariff On 1,371 China Product Categories






