-
Xibei Closes 102 Stores: Could These Outlets Have Been Saved Without Public Opinion Storms?

Starting on the afternoon of January 15th, news of Xibei closing 102 stores exploded in the catering industry, taking the form of a "confession" from founder Jia Guolong's WeChat Moments. This contraction, affecting over 30 cities, also marks the la
Huxiu Technology7 -
Latest! European Union (EU) To Impose Fixed Tariff Of 3 Euros Per Small Import Package Starting Next July! Plastic Prices Mixed Today

I. Latest! The EU is set to impose a fixed duty of 3 euros per small import parcel starting July next year. According to foreign media reports, EU finance ministers have agreed to impose a fixed tariff of 3 euros per package on imported pa
Plastmatch -
Over 28 Billion, Starbucks China Business 60% Stake Falls to Boyu: Will Operate Through Joint Venture, Headquarters Remains in Shanghai

The matter of Starbucks, the world's largest coffee chain, selling part of its business in China has finally come to a conclusion. Today, Starbucks announced a strategic partnership with Boyu Capital. Establish a joint venture.Jointly operate Starbu
Snack Era -
Porsche Temporarily Suspends EV Production! Chip Firm Innovates with Plastic Packaging from Used Cooking Oil

International News Highlights: Raw Material News- Integration of Plastic and Electronic Technology Empowering Smart Mobility: Multidimensional Innovation of Scootech Scooters. Recycling NewsTechnip Energies will promote the commercialization of plas
Plastmatch -
EU Cracks Down on Greece's Plastic Recycling Scandal: €11.9 Million Project Plunged Into Violation Maelstrom

The European Union's patience with Greece in the environmental protection sector is wearing thin. The European Public Prosecutor's Office (EPPO) recently announced a criminal investigation into plastic recycling projects in Athens, the Peloponnese, a
Plastmatch Global Digest -
Enjie Shares Reports First-Half Loss of 93.11 Million Yuan, Revenue Up 20.5% Year-on-Year

On August 18, Enjie Co., Ltd. (002812) released its half-year report for 2025. The company's operating revenue was 5.76 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 20.5%; net profit attributable to shareholders was a loss of 93.11 million yuan, a year-o
Cai Zhong News Agency -
No Label Again? Master Kong Tests "Naked Bottle"! Easy to Remove Labels, How Hard Is It to Break Habits? The Challenges of Popularizing Label-Free Water

Good packaging is not only an indispensable component of product competitiveness but also an important vehicle for conveying brand value and philosophy. The Pentawards, known as the "Oscars" of the packaging design industry, released the "2024-2025 P
Packaging Manager -
11 Billion Yuan Major Investment in the Packaging Industry!

On the evening of August 6, Xianhe Co., Ltd. (603733) announced that, following thorough on-site inspections and in-depth discussions, the company officially signed the "Investment Agreement for the Integrated High-Performance Paper-Based New Materia
Securities Times -
EFSA Approves Kreyenborg Infrared Technology for Food Packaging Recycling Materials

The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has issued a positive scientific opinion on the infrared technology IR-Clean developed by the German company Kreyenborg, in accordance with EU Regulation 2022/1616. This technology can decontaminate recycled
Plastmatch Global Digest -
Hefei Hengxin's July Surge: 500 Million for New Factory, 60 Million for Land, Another 40 Million Contract!

Amidst the global wave of sustainable development, Hefei Hengxin Life Technology Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as "Hengxin Life"), which focuses on the field of green degradable products, is accelerating its strategic layout. During July, the
Global Printing and Packaging Industry -
Moutai, wuliangye, luzhou laojiao, and fenjiu take the top four spots in the 2025 global spirits brand value top 50!
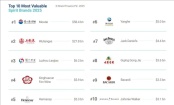
The UK brand evaluation agency "Brand Finance" released the "Alcoholic Drinks 2025" global brand value ranking. In the "Spirits 50" category, Chinese brands Moutai, Wuliangye, Luzhou Laojiao, and Fenjiu took the top four positions, while Yangh
Observation of the Food and Beverage Industry -
Packaging Basics | An Overview of "Perfume Pump" Manufacturing Process, Technical Principles, and Procurement Key Points

The perfume pump is a crucial precision component in perfume products, directly determining the user experience, shelf life, and brand image of the product. Below, I will provide a detailed introduction from six aspects: definition, functional st
Packaging Material Business Circle -
Heshun Technology: Emphasizing Differentiated Functional Film R&D

Heshun Technology (301237) announced that on July 22, 2025, the company held an investor relations event, primarily conducting research for specific targets. The event took place in the company's 11th-floor conference room, with participants includin
Cai Zhong News Agency -
Revealed! this european paper and packaging giant earns 15.6 billion annually and has three factories in china!

VPK Group, a leading packaging company founded in 1935 and headquartered in Belgium, has developed from a local enterprise into an international supplier of sustainable protective packaging solutions over the decades. Its core business revolves aro
Global Printing and Packaging Industry -
Overseas Highlights: PPG Establishes New Aerospace Coatings Plant in the US, Yizumi Turkey Company Officially Opens! Pepsi Adjusts Plastic Packaging Goals

News Headlines: Raw Materials News - $380 Million! PPG to Build New Aerospace Coatings Plant in the United States Automotive News - FF Officially Receives Factory and Operation Center in Ras Al Khaimah, UAE Packaging News-PepsiCo moves its sust
Specialized Plastic World -
"Over 40 Million Yuan Debt Forces Decision to Return Home and Take Over Family Luggage Factory"

In the second episode of the "Inheriting the Family Business Vlog," Shen Ruoyi recorded a scene of herself crying for the first time using her phone. That day, as the second generation who was to inherit the family business, she eagerly went to give
China Entrepreneur Magazine -
FURRONG New Materials Makes Impressive Debut at CHINAPLAS 2025 International Plastics & Rubber Exhibition, Enhancing Global Competitiveness!

On April 15, 2025, the CHINAPLAS 2025 International Plastics and Rubber Exhibition, themed "Transformation·Collaboration·Shaping Sustainability," grandly opened at the Shenzhen World Exhibition & Convention Center (Bao'an New Venue). Furon
Specialized Plastic World -
A leading domestic flexible packaging company sees a 90% drop in net profit.

However, behind the slight decline in revenue, the company is facing considerable pressure on its profitability.Nevertheless, the company's operating income in the third quarter was acceptable at 162 million yuan, second only to the fourth quarter's
Plastic Film Net -
Analysis of Modified Atmosphere Packaging Film Technology: Structural Design, Material Innovation, and Optimization of Food Preservation Processes

Analysis of Modified Atmosphere Packaging Film Technology: Structural Design, Material Innovation, and Food Preservation Process OptimizationResearch on the Development of High Barrier and Functionalized Food Packaging Films1. Structure and Function
Food Packaging Alliance -
Speed 700 meters/minute! The black tech behind this foreign company's new BOPP production line is revealed.

Oben Group is a globally leading manufacturer of packaging materials, primarily producing polypropylene (PP), polyester (PET), and nylon films.After acquiring KristaFilms in July 2023, the company plans to build a new production facility in Monterrey
Specialized Plastic Translation
Most Popular
-

Key Players: The 10 Most Critical Publicly Listed Companies in Solid-State Battery Raw Materials
-

Vioneo Abandons €1.5 Billion Antwerp Project, First Commercial Green Polyolefin Plant Relocates to China
-

EU Changes ELV Regulation Again: Recycled Plastic Content Dispute and Exclusion of Bio-Based Plastics
-

Clariant's CATOFIN™ Catalyst and CLARITY™ Platform Drive Dual-Engine Performance
-

List Released! Mexico Announces 50% Tariff On 1,371 China Product Categories






